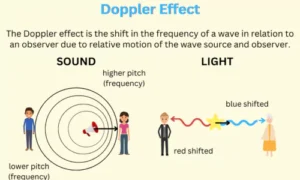
Have you ever noticed how the sound of a passing ambulance siren varies as it gets closer and farther away? The Doppler Effect explains this variation in frequency. The Doppler Effect is commonly associated with sound, but it also applies to light waves, making it one of the most significant instruments in astronomy.
What is the Doppler Effect?
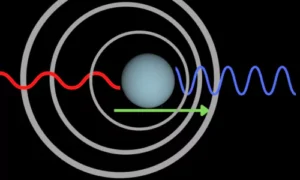
The Doppler Effect is the change in frequency or wavelength of a wave as the source and observer move relative to each other.
- If the source is moving towards the observer, the waves compress, and frequency increases (higher pitch in sound, blue shift in light).
- If the source is moving away, the waves stretch, and frequency decreases (lower pitch in sound, red shift in light).
Doppler Effect in Light (Astronomy)

When applied to light waves, the Doppler Effect becomes a powerful tool for astronomers:
- Blue Shift: Light from an object moving towards Earth shifts to shorter wavelengths (towards the blue end of the spectrum).
- Red Shift: Light from an object moving away shifts to longer wavelengths (towards the red end of the spectrum).
Uses of the Doppler Effect in Astronomy
1. Measuring the Motion of Stars and Galaxies
Astronomers study the shift in starlight to determine whether stars and galaxies are moving towards us (blue shift) or away from us (red shift).
2. Evidence for the Expanding Universe
Edwin Hubble observed that most galaxies show a red shift, meaning they are moving away. This provided strong evidence that the universe is expanding.
3. Detecting Exoplanets
The Doppler Effect helps in identifying planets orbiting distant stars. As the planet pulls on its star, the starlight shifts slightly due to the star’s wobble.
4. Measuring the Speed of Celestial Objects
By analysing frequency shifts, astronomers calculate the velocity of stars, galaxies, and even black holes relative to Earth.
5. Understanding Binary Star Systems
In systems with two stars orbiting each other, the Doppler Effect reveals their movement by showing alternating red and blue shifts in their light.
Everyday Example vs Astronomy
- On Earth: You hear the ambulance siren change pitch as it moves past you.
- In Space, Astronomers see light from galaxies shift in wavelength depending on their movement.
Conclusion:
The Doppler Effect is more than just a change in sound pitch; it provides a view into the universe. It remains one of the most powerful tools in astronomy, capable of establishing that galaxies are drifting apart and discovering planets outside our solar system. Scientists are still learning more about the velocity, structure, and evolution of the universe by examining light shifts.






https://ahpi.imweb.me/
August 20, 2025References:
Slotting machine
References:
https://ahpi.imweb.me/
https://visualpython.ai//?bmode=view&idx=16591420
August 20, 2025References:
Slots no download
References:
https://jhonmarkalbios.marketlevelseo.com/mastering-time-management-key-to-business-success/