Recently updated on May 4th, 2025 at 05:25 pm
Cosmology is the study of the universe, a field of astronomy that studies its overall features and structures. It investigates fundamental problems regarding the universe’s creation, evolution, and ultimate fate.
The scientific study of the universe’s beginnings, composition, development, and ultimate destiny is known as cosmology. In this regard, cosmologists study the Big Bang, dark matter, dark energy, and black holes to understand the universe comprehensively.
Moreover, this field explores issues related to the origins, growth, and invisible forces accelerating the cosmos. Specifically, the secrets of dark matter and dark energy, which together make up 95% of the universe, are being explored by scientists using sophisticated instruments like telescopes, particle accelerators, and computer simulations.
The study of cosmology, which addresses some of the most difficult and fundamental issues of existence, is an extensive topic. Some of its main facets and subfields are as follows:
1. The Big Bang Theory and Origins in the Universe

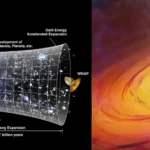
Cosmology studies the universe’s beginnings, which are generally believed to have started with the Big Bang, an explosive expansion that took place some 13.8 billion years ago.
According to the Big Bang Theory, Initially, the universe began as an extremely hot and dense state and has since been expanding. To learn more about this, cosmologists examine the cosmic microwave background (CMB), which is the feeble radiation that remains after the Big Bang.
2. Structure and Evolution

Galaxies, galaxy clusters, and superclusters are all part of the universe’s large-scale structure. Cosmologists investigate the formation and interactions of these structures. For instance, galaxies are found in clusters rather than dispersed uniformly and are sculpted by gravity, dark matter, and other reasons. Scientists can learn more about the evolution of matter over billions of years by examining these formations.
3. Dark Energy and Dark Matter in the Universe

Only around 5% of the universe is composed of “ordinary” matter, or the atoms that make up stars, planets, and life itself. Indeed, this is a startling discovery in cosmology. In contrast, however, mysterious elements known as dark matter (about 27%) and dark energy (roughly 68%) make up the remaining 95%.
Furthermore, although dark matter is invisible because it neither emits nor absorbs light, it, nevertheless, affects visible matter through mass and gravity. On the other hand, dark energy is believed to be the cause of the universe’s accelerated expansion, which is driving galaxies farther apart at an accelerating pace. One of the biggest problems in cosmology is trying to understand these elements.
4. Strange Items and Black Holes

Additionally, black holes, areas of spacetime whose gravity is so great that not even light can escape, are another topic covered in cosmology. Specifically, supermassive black holes, which are found at the core of the majority of galaxies, are crucial to the development and behaviour of galaxies.
White holes, which are the theoretical opposites of black holes, and wormholes, which are hypothetical routes through spacetime, are examples of exotic theoretical objects that continue to be the subject of discussion and interest.
5. The Universe’s Destiny

The study of cosmology delves into various possibilities for the final fate of the cosmos, including:
- If dark energy continues to expand the universe, the result will be a cold and dark cosmos as galaxies grow increasingly distant from one another, eventually causing their stars to burn out.
- A singularity may form and potentially trigger a second Big Bang if the universe’s expansion eventually halts and reverses, resulting in the Big Crunch.
- Dark energy could potentially grow so powerful that it rips apart stars, galaxies, and even atoms, leading to a dramatic disintegration of the cosmos known as the Big Rip.
6. The Inflation of the Cosmos in the Universe

The universe expanded exponentially and quickly in its early stages, according to the cosmic inflation theory, even surpassing the speed of light. This idea explains the observable homogeneity of the universe on enormous scales. During inflation, quantum fluctuations may have led to the formation of the first galaxies, resulting in the current large-scale structure.
7. Theories of the Multiverse and Astrobiology

In astrobiology, the study of possible extraterrestrial life overlaps with cosmology. The theory of a multiverse is investigated by certain cosmologists. In the absence of definitive evidence, several regions or “bubble universes,” each with distinct physical laws, constants, or dimensions, might exist as part of a multiverse.
Instruments and Methods in Cosmology
Exploring the fate of the cosmos, cosmology considers potential outcomes like:
- Firstly, telescopes allow scientists to see far into space and time, particularly through observatories like the Hubble Space Telescope and the upcoming James Webb Space Telescope.
- Secondly, particle accelerators also assist in the study of fundamental particles and forces. For instance, the Large Hadron Collider reveals insights into conditions similar to those existing right after the Big Bang.
- Moreover, computer simulations aid in testing theories regarding the influence of dark matter and dark energy, as well as the genesis of structures, by replicating robustly the cosmic evolution.”
Everything in the universe has “big questions” concerning its creation, nature, and destiny answered through cosmology, which combines theories with observations. Our efforts expand our knowledge of the universe and strengthen our sense of place within it.
Conclusion:
The universe, with its vast complexity and endless mysteries, continues to enchant humans. The discovery of the cosmos, from the beginnings of galaxies to the nature of dark matter and energy, broadens our scientific knowledge.
From the beginnings of galaxies to the nature of dark matter and energy, our discovery of the cosmos not only broadens scientific knowledge. Our creation of new tools and approaches also raises questions about our philosophical concept of existence.
Cosmic events provide us with deeper insights, paving the way for future discoveries. This magnificent tapestry of existence inspires scientists with its intrigue, sparks curiosity, and reminds us of our place, as we continue our efforts to understand it.






smorter giremal
September 26, 2024It is really a nice and helpful piece of information. I am satisfied that you just shared this helpful info with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thank you for sharing.