The human brain is the body’s most powerful organ, controlling ideas, emotions, movements, and crucial survival functions. To understand how it operates, we must investigate its structure and anatomy. The brain is made up of many areas, each specialised for a specific function.
Also See: Brain Disorders and Diseases
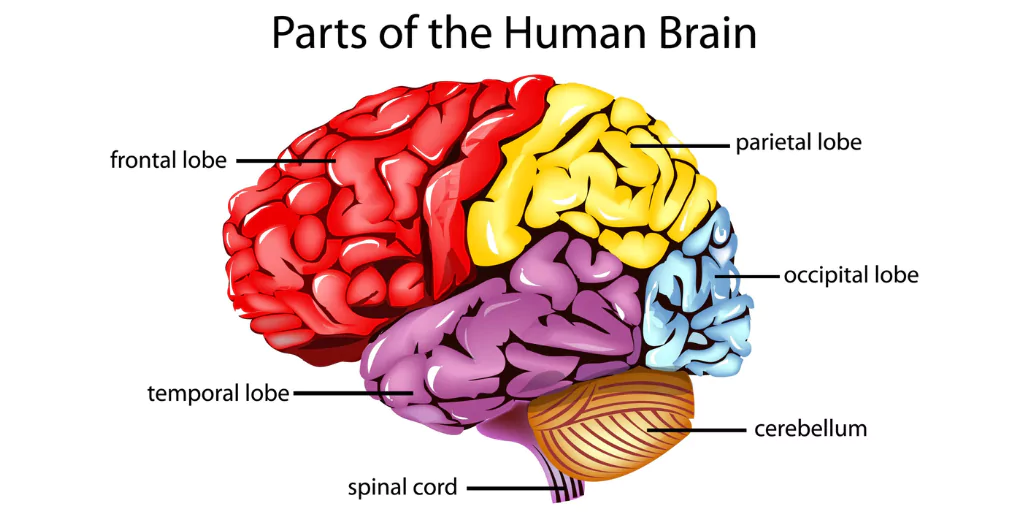
Major Parts of the Brain
1. Cerebrum
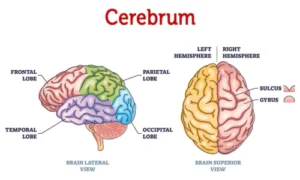
The largest part of the brain.
Divided into two hemispheres (left and right).
Each hemisphere is further divided into lobes:
- Frontal Lobe – decision-making, reasoning, emotions, voluntary movements.
- Parietal Lobe – sensory processing (touch, temperature, pain).
- Temporal Lobe – hearing, language, memory.
- Occipital Lobe – vision and image interpretation.
2. Cerebellum
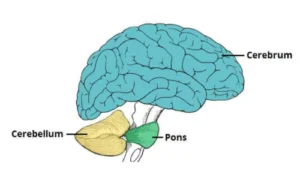
- Located in the back of the brain, beneath the cerebrum.
- Maintains balance, posture, and coordination.
- Ensures the smooth execution of voluntary actions.
3. Brainstem
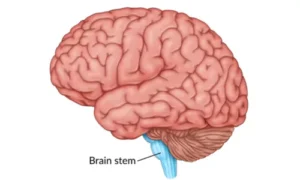
- Connects the brain and spinal cord.
- It is divided into the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata.
- Controls autonomic functions, including breathing, heart rate, swallowing, and sleep patterns.
4. Limbic System
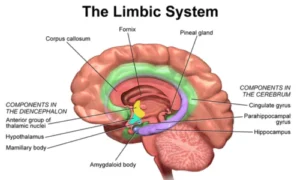
- Known as the “emotional brain.”
- Main structures include the amygdala, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and thalamus.
- Functions include emotion, memory formation, learning, and motivation.
5. Cerebral Cortex
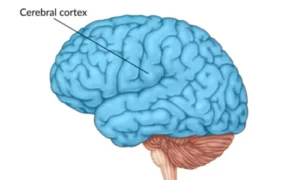
- The cerebrum’s outer layer is composed of grey matter.
- Responsible for higher-level thinking, problem-solving, language, and creativity.
Protective Layers of the Brain
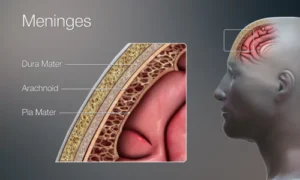
The brain is delicate and protected by multiple layers:
- Skull – hard outer bone.
- Meninges – three protective membranes: dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater.
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) – cushions the brain, prevents injury, and removes waste.
Neurons are the building blocks of the brain
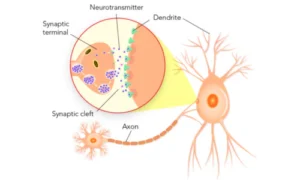
- The brain contains around 86 billion neurons.
- Neurons interact using both electrical and chemical signals.
- Glial cells help supply nutrients, insulation, and structural support.
Interesting facts about brain anatomy
- The left hemisphere regulates the right side of the body, and vice versa.
- The brain consumes roughly 20% of the body’s overall oxygen supply.
- Despite its tiny size, the cerebellum is home to more than half of the brain’s neurons.
Conclusion
The structure and anatomy of the brain demonstrate how intricate and strong this organ is. Each region has an important part in our survival, thoughts, emotions, and behaviours. Scientists are still discovering the mysteries of human intelligence and consciousness through brain research.