Have you ever noticed something strange?
The moment you step into a swimming pool:
Your body feels lighter
Standing becomes easier
Jumping feels slow and floaty
But the moment you come out:
Your body feels heavy again
So what changed?
Your weight did not change.
Gravity did not disappear.
Then why does your body feel lighter in water?
This everyday experience is explained by a beautiful physics concept called buoyancy.
In this article, you’ll understand:
Why do we feel lighter in water
What buoyancy really means
Swimming and daily-life examples
Simple explanations with zero heavy maths
Do We Actually Become Lighter in Water?
Let’s clear the biggest doubt first.
- No, your actual weight does not reduce in water.
- But your effective weight becomes less.
That difference between real weight and felt weight is the key idea of this topic.
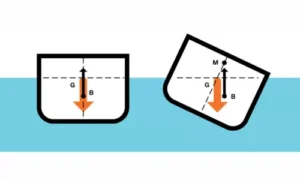
What Is Buoyancy?
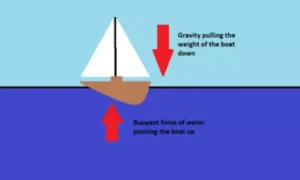
Buoyancy is the upward push given by a liquid (like water) on an object placed inside it.
In simple words:
- Water pushes objects upward when they are inside it.
- This upward push acts against gravity, making objects feel lighter.
Why Does Water Push Objects Upward?
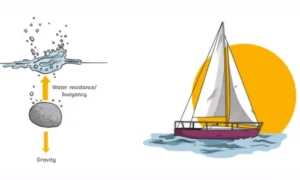
Water is not space.
It has:
Mass
Weight
Pressure
When you enter water:
Water pushes from all sides
The upward push is slightly stronger than the downward push
This creates an upward force, which supports your body.
That support is why you feel lighter.
A Simple Way to Imagine Buoyancy
Imagine you are carrying a heavy bag alone.
Now imagine two people carrying the same bag.
Your effort reduces because:
The load is shared
In water:
Gravity pulls you downward
Water shares the load by pushing you upward
Result: You feel lighter.
Why Is Standing Easy in a Pool?

On land:
Your entire weight acts on your legs
In water:
Water pushes your body upward
Legs carry only part of your weight
That’s why:
Standing feels easy
You can balance better
Why Can We Jump Higher in Water?

Actually, you don’t jump higher—you fall slower.
Water:
Reduces effective weight
Resists motion
So your movement looks slow and floaty.
Why Do We Float Better When Lying Flat?

When you lie flat in water:
More body surface touches water
Water pushes a larger area upward
This increases buoyancy, making floating easier.
That’s why swimming instructors teach beginners to:
Buoyancy in Swimming

Swimming is possible because of two things:
Buoyancy
Body movement
Buoyancy:
Prevents you from sinking immediately
Swimming actions:
Help you move forward
Without buoyancy:
Humans would sink like stones
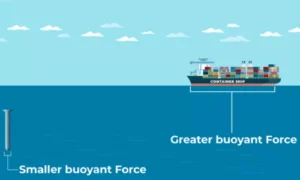
Why Do Heavy Objects Sink but Ships Float?

This confuses many students.
A ship:
Is very heavy
But has a large hollow space
This allows it to:
Displace a large amount of water
Get a strong upward push
So floating depends on shape and water displacement, not just weight.
Daily Life Examples of Buoyancy
A stone sinks in water
A plastic bottle floats
Oil floats on water
Life jackets help people float
All of these are the result of buoyant force.
Buoyancy vs Weight
| Concept | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Weight | Downward pull by gravity |
| Buoyancy | Upward push by water |
| On land | Only weight acts |
| In water | Weight + upward buoyant push |
| Result | Body feels lighter |
Does Buoyancy Work Only in Water?
No.
Buoyancy works in:
Water
Oil
Air (yes, even air!)
Example:
Hot air balloons float in the air due to buoyancy
But buoyancy is strongest in liquids because they are denser than air.
Why Students Get Confused About This Topic
1. Mixing Weight and Mass
Students think:
Feeling lighter = less weight
But weight stays the same.
2. Overthinking Formulas
Buoyancy is often taught with formulas, which scares students.
But understanding:
Direction of forces
Simple reasoning
It is enough at the school level.
3. Not Connecting to Real Life
Once you imagine:
A swimming pool
The concept becomes obvious.
Where This Comes in Exams

This topic appears in exams as:
1. Conceptual Questions
Why do we feel lighter in water?
What is buoyancy?
2. Reason-Based Questions
Why can ships float?
Why does a stone sink?
3. Assertion–Reason
Assertion: A body feels lighter in water
Reason: Water exerts an upward force
4. MCQs
Identifying buoyancy
Floating vs sinking situations
Mostly theory-based, not numerical-heavy.
Quick Revision Points

Weight does not change in water
Buoyancy is an upward force
Water supports part of the body’s weight
More water displaced → more buoyancy
Swimming is possible because of buoyancy
Conclusion
Feeling lighter in water is one of the best examples of physics in daily life.
You don’t need equations to understand it—just imagine:
Gravity is pulling you down
Water gently pushing you up
That balance creates the magic feeling of floating.
Once you understand buoyancy, swimming, floating, and ships all make sense.