In the field of physics and motion, the concept of velocity is critical to understanding how objects move. While many people use the terms speed and velocity interchangeably, in science, they have different meanings. Velocity indicates not only how quickly an object is going, but also in which direction. Let’s look at the genuine definition of velocity, its various sorts, calculations, and applications in everyday life.
What is velocity?
Velocity is defined as an object’s rate of change in displacement over time. Simply said, it explains how quickly an object goes in a specific direction.
- Speed simply gives us the magnitude (how quickly).
- Velocity indicates both magnitude and direction.
So, if a car moves at 60 km/h toward the north, its velocity is 60 km/h north.
Formula for Velocity
The general formula for velocity is: v=Δx/Δt
Where:
v = velocity
Δx = displacement (change in position)
Δt = time taken
Example:
If a runner covers 100 meters east in 10 seconds,
v=100/10=10 m/s east
Types of Velocity

1. Uniform velocity:
When an object travels in a straight line, its velocity is uniform because it makes equal displacements at equal time intervals.
Example: An automobile travelling at 60 km/h on a straight route.
2. Variable Velocity:
When the speed or direction (or both) of motion changes over time, the velocity is said to be variable.
Example: Consider an automobile making turns at different speeds.
3. Average velocity:
It equals the entire displacement divided by the total time taken.
v=Total Displacement/Total Time
4. Instantaneous velocity:
The velocity of an object at a specific moment in time.
Difference Between Speed and Velocity
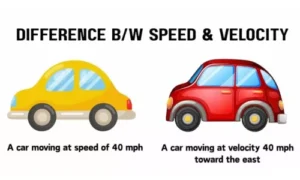
| Aspect | Speed | Velocity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rate of change of distance | Rate of change of displacement |
| Type | Scalar quantity | Vector quantity |
| Direction | No direction | Has direction |
| Example | 60 km/h | 60 km/h east |
Graphical Representation of Velocity
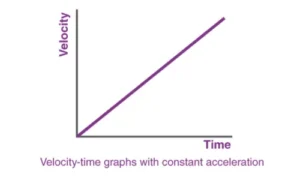
- A displacement-time graph can represent velocity.
- A straight line represents uniform velocity.
- A curving line indicates that the velocity is changing (either increasing or decreasing).
Uses of Velocity in Daily Life

- Transportation: Calculates journey time and route direction.
- Sports: Used to assess athlete performance (e.g., sprinters, cyclists).
- Engineering contributes to the creation of safe and efficient automobiles.
- Astronomy: Determines the velocity and direction of planets and stars.
- Weather forecasting is used to anticipate wind velocity and storm motions.
Conclusion
Velocity means more than just “speed.” It describes the rate and direction of motion, making it an important topic in physics, engineering, and everyday life. Everything in motion, from automobiles on the highway to planets orbiting the sun, has velocity. Understanding it allows us to forecast motion, calculate journey times, and create systems that move efficiently.