How do plants produce their own food? Have you ever wondered? One of the most incredible natural phenomena, photosynthesis, holds the key to the solution! It is the process by which plants generate the energy required for growth and survival by utilising sunlight, water, and air.
1. What is photosynthesis?

Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and certain microbes transform sunlight into chemical energy. Plants use chlorophyll, a green pigment, to absorb sunlight, CO₂ from the air, and H₂O from the soil. What was the result? They produce glucose (a sugar) and release oxygen (O₂) into the air.
In simpler terms:
- Sunlight + Water + Carbon Dioxide → Glucose + Oxygen
Why is photosynthesis important?
- Oxygen for Life: It provides the oxygen we breathe.
- Food for All: Plants provide energy for all living beings, making them the foundation of the food chain.
- Climate Balance: Plants help to remove carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, keeping our world cool.
2. What is artificial photosynthesis?

Artificial photosynthesis is a man-made replica of the natural mechanism that plants use. Scientists utilise solar panels, catalysts, and chemical systems to simulate how plants receive and transform sunlight into energy.
Instead of creating plant food (glucose), artificial photosynthesis seeks to generate clean fuels such as hydrogen or methanol, which can power vehicles, companies, and houses while lowering pollution.
How Does it Work?
- Light Absorption: Special materials operate like chlorophyll to absorb sunlight.
- Water Splitting: The system converts water (H₂O) to hydrogen and oxygen.
- Fuel Production: Hydrogen may be stored or used to produce environmentally acceptable fuels.
3. Photosynthesis and Carbon Dioxide
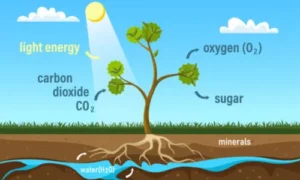
Plants use carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the air to make glucose and oxygen through photosynthesis. Plants operate as natural air cleaners, minimising heat-trapping effects in our environment by absorbing CO₂, a primary greenhouse gas.
In short:
- More plants → Less CO₂ → Cooler Earth
Impact on Climate and Ecosystems
- Forest protection helps combat climate change by absorbing large volumes of CO₂.
- Soil Health: Photosynthesis promotes plant development, which protects the soil from erosion.
- Water Cycle Regulation: Healthy plants and forests influence rainfall patterns, reducing floods.
- Photosynthesis, which produces energy for plants, indirectly supports herbivores and the entire food chain.
4. How Photosynthesis Impacts Climate and the Environment

Photosynthesis is not only a plant’s food production process, but also a vital instrument for maintaining our planet’s health. Plants use photosynthesis to eliminate pollution, balance the atmosphere, and combat climate change. Let’s look at how this basic green process influences our climate and ecosystem.
Photosynthesis and Carbon Balance
- Trees and plants are natural “carbon sinks” that absorb CO₂.
- Less CO₂ equals less heat trapped in the atmosphere, therefore reducing the greenhouse effect.
- Prevents Climate Change: Forests and oceans work together to keep our planet’s temperature stable.
Conclusion
Photosynthesis is nature’s heartbeat. It keeps our planet alive by giving food, oxygen, and ecological balance. Without this incredible process, life on Earth would not exist as we know it. So, the next time you see a green leaf soaking up the sun, remember that it is not only growing, but also powering the entire planet!






