Recently updated on September 25th, 2025 at 09:37 am
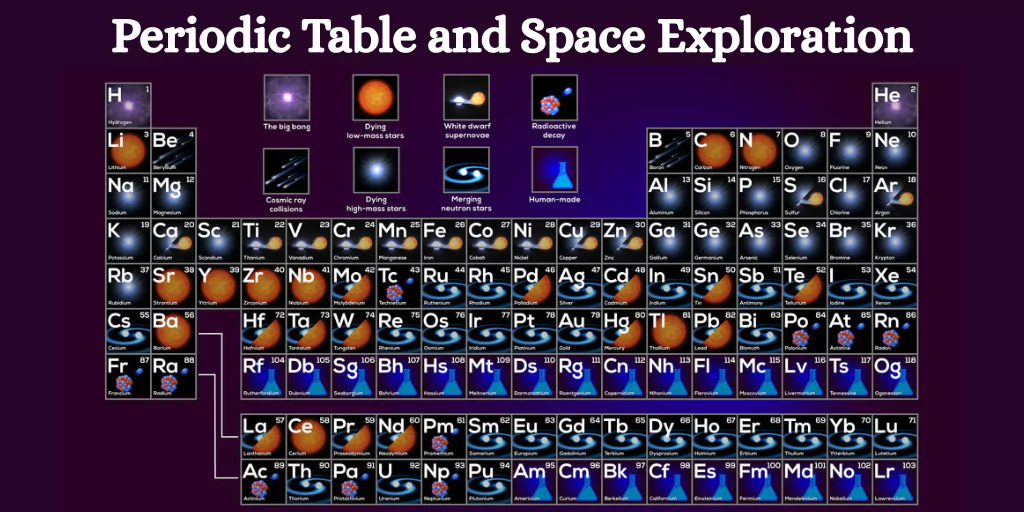
The periodic table is not only an essential part of chemical education, but it also serves as a reference for space exploration. Every rocket, spacecraft, satellite, and astronaut mission is reliant on materials and elements listed in the periodic table. Scientists and engineers may construct stronger spaceships, develop more efficient fuels, and even look for indications of life beyond Earth by analysing element properties.
Role of the Periodic Table in Space Exploration
1. Rocket Fuels and Propulsion
Hydrogen and oxygen are important components of rocket fuel. Combining liquid hydrogen (LH₂) and liquid oxygen (LOX) generates tremendous thrust, serving as the foundation for space launches. Solid rocket boosters also utilise other materials, such as aluminium.
2. Materials for Spacecraft
Spacecraft must resist extreme temperatures, cold, and radiation. Materials based on titanium, aluminium, and carbon composites are preferred for their strength and lightweight qualities. The periodic chart helps scientists determine which elements can withstand severe space conditions.
3. Life Support Systems
Astronauts rely on oxygen (O) to breathe, carbon (C) for food and energy, and nitrogen (N) to keep the cabin pressure stable. The periodic table determines how these elements interact and how they can be recycled on the International Space Station (ISS).
4. Protecting Against Radiation
Space is rife with hazardous cosmic rays and solar radiation. Lead (Pb) and boron (B) are being explored for shielding, while improved polymers and nanostructures based on carbon can assist in safeguarding astronauts.
5. Searching for Life on Other Planets
The periodic table is used by scientists to hunt for critical elements, including carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and sulfur (CHNOPS). Finding them on Mars, Europa, or exoplanets enhances the odds of discovering life beyond Earth.
6. Creating New Elements in Space Research
Superheavy elements, which are added to the far end of the periodic table, are occasionally created in particle accelerators. Space exploration motivates research into whether such substances can exist naturally in harsh cosmic conditions.
Future Possibilities

- Mining rare elements such as helium-3 from the Moon to generate fusion energy.
- Using asteroid metals (nickel, iron, and platinum) to build spacecraft.
- Discovering previously unknown elements in faraway galaxies.
Conclusion
The periodic table is more than just a classroom chart; it’s a road map for space exploration. From rocket fuel and spacecraft architecture to astronaut protection and the search for extraterrestrial life, the elements govern humanity’s journey into space. As we explore deeper into the universe, the periodic table remains our most reliable instrument for discovery.