Light & Optics are among the most fascinating areas of physics. Light allows us to see the world around us, while optics studies how it interacts with objects and surfaces. From the reflection in mirrors to the power of microscopes and telescopes, light & optics explain it all.
Reflection of Light

Reflection is the bouncing back of light when it strikes a smooth surface, such as a mirror.
Laws of Reflection:
- The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
- The incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal all lie in the same plane.
Examples in real life: mirrors, shiny surfaces, still water, and polished metals.
Lenses and Their Uses
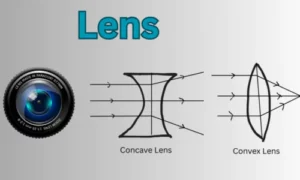
A lens is a transparent material (usually glass or plastic) that refracts light to converge or diverge rays.
- Convex Lens (Converging lens): Brings light rays together; used in magnifying glasses, cameras, microscopes, and telescopes.
- Concave Lens (Diverging lens): Spreads out light rays; used in spectacles for people with myopia (short-sightedness).
Lens Formula: 1/f = 1/v – 1/u
where f = focal length, v = image distance, and u = object distance.
Telescopes

A telescope is an optical instrument used to observe distant objects, especially in astronomy.
- Refracting Telescope: Uses lenses to bend and focus light.
- Reflecting Telescope: Uses mirrors instead of lenses.
Application: studying planets, stars, and galaxies. Telescopes have opened the window to space exploration.
Microscopes
A microscope magnifies tiny objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye.
- Simple Microscope: Uses a single convex lens (like a magnifying glass).
- Compound Microscope: Uses two or more lenses to achieve higher magnification.
Application: biology, medicine, nanotechnology—helping us study cells, bacteria, and microscopic structures.
Refraction of Light: Principles, Uses & Phenomena
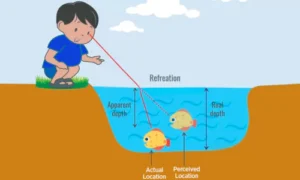
Have you ever noticed that a pencil bends when placed in a glass of water? Or why do stars appear to twinkle at night? These intriguing phenomena result from light refraction. Refraction is a fundamental concept in optics that describes how light behaves when it moves from one material to another.
What is Refraction of Light?
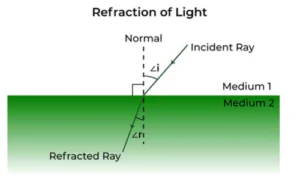
Refraction is the bending of light rays when they travel from one medium to another (for example, from air to water or glass). This bending occurs because the speed of light changes in different media.
- Light travels fastest in air (or vacuum).
- It slows down in denser media like water or glass.
Principles of Refraction
1. Change in Speed Causes Bending
- When light enters a denser medium (air → water), it slows down and bends towards the normal.
- When it moves to a rarer medium (water → air), it speeds up and bends away from the normal.
2. Laws of Refraction (Snell’s Law):
- The incident ray, the refracted ray, and the normal all lie in the same plane.
- The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant:
n1 sin θ1=n2 sin θ2
where n is the refractive index of the medium.
Everyday Examples of Refraction

- A straw or pencil appears bent in a glass of water.
- The twinkling of stars (light bends as it passes through layers of air).
- A pool appears shallower than its actual depth.
- The rainbow, formed due to the refraction and dispersion of light in water droplets.
Uses of Refraction
- Lenses in Glasses and Contact Lenses – Correcting vision problems like myopia (short-sightedness) and hypermetropia (long-sightedness).
- Cameras and Projectors – Use refraction to focus images.
- Microscopes & Telescopes – Use lenses to magnify small objects or observe distant celestial bodies.
- Fibre Optics – Uses refraction and total internal reflection for fast data transmission.
- Prisms & Rainbows – Refraction helps in separating white light into different colours.
Phenomena Related to Refraction
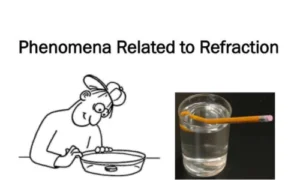
- Apparent Depth: Objects in water look closer than they are.
- Mirages: Optical illusions in deserts or hot roads caused by the refraction of light through air layers of different temperatures.
- Dispersion of Light: Splitting of white light into colours when it passes through a prism.
- Total Internal Reflection (TIR): When light reflects entirely inside a medium instead of refracting—used in optical fibres and diamonds.
Conclusion
Light and optics not only help us understand natural phenomena but also drive modern technology. From mirror reflections and water refraction to lenses in eyeglasses, telescopes that explore the universe, and microscopes that reveal the microscopic world—optics is everywhere. Refraction, too, is more than a classroom concept; it surrounds us in daily life, from rainbows and eyeglasses to telescopes and fibre-optic internet. Together, these principles connect the wonders of nature with the innovations that shape our future.
FAQs on Light & Optics
Q1. What is the difference between reflection and refraction?
Reflection is the bouncing back of light from a surface, while refraction is the bending of light when it enters a new medium.
Q2. Why do stars twinkle at night?
Stars twinkle because their light gets refracted multiple times while passing through the Earth’s atmosphere.
Q3. Which lens is used in magnifying glasses?
A convex lens is used in magnifying glasses to converge light rays and enlarge images.
Q4. How is a telescope different from a microscope?
A telescope is used to observe distant objects like stars and planets, while a microscope is used to magnify very small objects like cells and bacteria.
Q5. What are some daily life examples of lenses?
Spectacles, cameras, magnifying glasses, projectors, and binoculars all use lenses.






FrankPeemy
August 20, 2025Equilibrado de piezas
El equilibrado representa una fase clave en el mantenimiento de maquinaria agricola, asi como en la fabricacion de ejes, volantes, rotores y armaduras de motores electricos. Un desequilibrio provoca vibraciones que aceleran el desgaste de los rodamientos, provocan sobrecalentamiento e incluso pueden causar la rotura de los componentes. Para evitar fallos mecanicos, resulta esencial detectar y corregir el desequilibrio a tiempo utilizando tecnicas modernas de diagnostico.
Principales metodos de equilibrado
Hay diferentes tecnicas para corregir el desequilibrio, dependiendo del tipo de componente y la intensidad de las vibraciones:
Equilibrado dinamico – Se aplica en elementos rotativos (rotores, ejes) y se lleva a cabo mediante maquinas equilibradoras especializadas.
El equilibrado estatico – Se usa en volantes, ruedas y otras piezas donde es suficiente compensar el peso en un unico plano.
La correccion del desequilibrio – Se lleva a cabo mediante:
Perforado (retirada de material en la zona de mayor peso),
Colocacion de contrapesos (en ruedas y aros de volantes),
Ajuste de masas de balanceo (por ejemplo, en ciguenales).
Diagnostico del desequilibrio: equipos utilizados
Para identificar con precision las vibraciones y el desequilibrio, se emplean:
Maquinas equilibradoras – Permiten medir el nivel de vibracion y determinan con exactitud los puntos de correccion.
Analizadores de vibraciones – Registran el espectro de oscilaciones, detectando no solo el desequilibrio, sino tambien fallos adicionales (por ejemplo, el desgaste de rodamientos).
Sistemas de medicion laser – Se usan para mediciones de alta precision en mecanismos criticos.
Las velocidades criticas de rotacion requieren especial atencion – condiciones en las que la vibracion se incrementa de forma significativa debido a la resonancia. Un equilibrado correcto previene danos en el equipo en estas condiciones de funcionamiento.
онлайн казино игры
August 20, 2025все казино игры Gates of Olympus —
Gates of Olympus — известный онлайн-слот от Pragmatic Play с системой Pay Anywhere, цепочками каскадов и коэффициентами до ?500. Действие происходит в мире Олимпа, где Зевс усиливает выигрыши и делает каждый раунд динамичным.
Сетка слота имеет формат 6?5, а выплата начисляется при появлении не менее 8 совпадающих символов без привязки к линиям. После расчёта комбинации символы удаляются, их заменяют новые элементы, активируя цепочки каскадов, которые могут дать несколько выплат за одно вращение. Слот считается игрой с высокой волатильностью, поэтому способен долго молчать, но при удачных раскладах может принести большие выигрыши до 5000? ставки.
Чтобы разобраться в слоте доступен демо-режим без финансового риска. При реальных ставках целесообразно использовать проверенные казино, например MELBET (18+), ориентируясь на RTP около 96,5% и правила выбранного казино.
онлайн азартные игры
August 20, 2025олимпус играть бесплатно
Слот Gates of Olympus — популярный онлайн-слот от Pragmatic Play с системой Pay Anywhere, каскадными выигрышами и усилителями выигрыша до ?500. Игра проходит на Олимпе, где верховный бог усиливает выигрыши и делает каждый раунд непредсказуемым.
Экран игры представлено в виде 6?5, а комбинация формируется при появлении 8 и более одинаковых символов без привязки к линиям. После расчёта комбинации символы пропадают, сверху падают новые элементы, запуская каскады, дающие возможность получить дополнительные выигрыши за одно вращение. Слот относится высоковолатильным, поэтому способен долго молчать, но в благоприятные моменты может принести большие выигрыши до 5000? ставки.
Чтобы разобраться в слоте доступен демо-версия без вложений. Для ставок на деньги целесообразно рассматривать лицензированные казино, например MELBET (18+), ориентируясь на показатель RTP ~96,5% и условия конкретной платформы.
Numbershop
August 20, 2025play slot games online Gates of Olympus slot —
Слот Gates of Olympus — популярный онлайн-слот от Pragmatic Play с системой Pay Anywhere, цепочками каскадов и коэффициентами до ?500. Игра проходит у врат Олимпа, где бог грома активирует множители и превращает каждое вращение случайным.
Сетка слота имеет формат 6?5, а комбинация начисляется при выпадении 8 и более совпадающих символов в любой позиции. После расчёта комбинации символы исчезают, на их место опускаются новые элементы, запуская каскады, способные принести несколько выплат за одно вращение. Слот относится волатильным, поэтому не всегда даёт выплаты, но при удачных раскладах даёт крупные заносы до ?5000 от ставки.
Чтобы разобраться в слоте доступен бесплатный режим без финансового риска. Для ставок на деньги стоит рассматривать проверенные казино, например MELBET (18+), принимая во внимание RTP около 96,5% и условия площадки.
Armandotum
August 20, 2025Buy Psychedelics Online
TRIPPY 420 ROOM operates as a dedicated online psychedelics dispensary, designed to provide consistently high-grade medical products covering a wide range of categories.
Before placing an order for psychedelic, cannabis, stimulant, dissociative, or opioid products online, customers are presented with a clear structure including product access, delivery methods, and assistance. The catalog includes 200+ products in various formats.
Shipping is quoted based on package size and destination, offering both regular and express delivery options. Each order includes access to a hassle-free returns system and a strong focus on privacy and security. Guaranteed stealth delivery worldwide is a core element, without additional charges. Every order is fully guaranteed to support reliable delivery.
The catalog spans cannabis flowers, magic mushrooms, psychedelic products, opioid medications, disposable vapes, tinctures, pre-rolls, and concentrates. All products are shown with transparent pricing, and visible price ranges for products with multiple options. Educational material is also provided, with references including “How to Dissolve LSD Gel Tabs”, and direct access to buy LSD gel tabs and buy psychedelics online.
The business indicates its office location as United States, CA, while maintaining several contact options, including phone, WhatsApp, Signal, Telegram, and email. The service highlights 24/7 express psychedelic delivery, positioning the dispensary around accessibility, discretion, and consistent customer support.
CharlesHus
August 20, 2025slot gacor situs toto situs toto 4d
폰테크
August 20, 2025폰테크
모바일 폰테크란 휴대폰을 이용해 빠르게 현금을 확보하는 공식적인 재테크 방식입니다. 일반적인 소비 목적의 휴대폰 사용과는 달리 통신 구조와 유통 경로를 이용해 현금을 확보하는 구조를 가지고 있으며, 진행 과정이 간단하고 진입 장벽이 낮다는 장점이 있습니다. 신용 문제로 금융권 이용이 어렵거나 급전이 필요한 상황에서 대안적인 방법으로 활용되는 경우가 많습니다.
폰테크의 기본적인 진행 방식은 비교적 간단합니다. 먼저 통신사를 통해 스마트폰을 정상적으로 개통한 뒤, 해당 단말기를 매입 업체를 통해 처분합니다. 가격은 모델과 시장 시세, 조건에 따라 달라지며, 정산 금액은 현금이나 계좌로 받게 됩니다. 이후 휴대폰 할부금과 통신요금은 본인이 정상적으로 납부해야 하며, 요금 관리가 핵심 요소입니다. 해당 방식은 불법 금융과는 다르며, 휴대폰을 하나의 자산처럼 활용하는 방식이라고 볼 수 있습니다.
기존 금융권 대출과 비교하면 뚜렷한 차이가 있습니다. 신용 심사나 서류 제출 부담이 적고, 단시간 내 자금 마련이 가능하다는 점이 가장 큰 특징입니다. 또한 대출 기록이 남지 않는 구조이기 때문에 기존 금융 기록이 부담되는 상황에서도 활용할 수 있습니다. 하지만 통신요금 미납이나 연체가 발생할 경우 신용도에 영향을 줄 수 있으므로 책임 있는 이용이 필수적입니다.
이 방식을 선택하는 배경은 여러 가지입니다. 급전이 필요한 상황이나 금융 이용이 제한된 경우, 자금 흐름이 필요한 상황 등 다양한 상황에서 고려됩니다. 즉각적인 현금 흐름이 중요한 경우에 실질적인 선택지로 평가됩니다.
확보한 현금은 주식이나 코인 투자, 사업 자금, 생활비 등 다양한 용도로 사용되기도 합니다. 다만 자금 사용에 대한 책임은 모두 본인에게 있으며, 투자에는 항상 손실의 가능성이 존재한다는 점을 충분히 인지해야 합니다. 폰테크는 수익을 보장하는 수단이 아니라 자금 확보 목적의 수단이라는 점을 명확히 해야 합니다.
폰테크는 합법적인 구조이지만 주의해야 할 부분도 분명히 존재합니다. 과도한 휴대폰 개통은 통신사 제재의 대상이 될 수 있으며, 상환 계획 없는 이용은 오히려 리스크가 됩니다. 또한 고수익을 보장하거나 명의 대여를 요구하는 업체는 피해야 하며, 절차는 항상 합법적이고 투명하게 진행되어야 합니다.
결론적으로, 해당 방식은 통신 구조를 이용한 정상적인 자금 마련 수단으로, 충분한 이해와 책임 있는 관리가 동반될 경우 현금 유동성 확보에 유용할 수 있습니다. 가장 중요한 것은 충분한 정보와 합리적인 결정입니다.
WalterBah
August 20, 2025폰테크
dolly4d
August 20, 2025togel dolly4d
Josephgon
August 20, 2025dispositivo de vitalidad
pg slot
August 20, 2025ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg
แพลตฟอร์ม TKBNEKO เป็นแพลตฟอร์มเกมออนไลน์ ที่ วางระบบโดยยึดการใช้งานจริงของผู้เล่นเป็นแกนหลัก. หน้าเว็บหลัก แสดงเงื่อนไขแบบเป็นตัวเลขตั้งแต่แรก: ฝากขั้นต่ำ 1 บาท, ขั้นต่ำถอน 1 บาท, เวลาฝากประมาณ 3 วินาที, และ ไม่จำกัดยอดถอน. ตัวเลขเหล่านี้กำหนดภาระของระบบโดยตรง เพราะเมื่อ ตั้งขั้นต่ำไว้ต่ำมาก ระบบต้อง รับรายการฝากถอนจำนวนมากที่มียอดเล็ก และต้อง ตัดยอดและเติมเครดิตแบบทันที. หาก การยืนยันเครดิตใช้เวลานานเกินไม่กี่วินาที ผู้ใช้จะ กดซ้ำ ทำให้เกิด รายการซ้อน และ เพิ่มโหลดฝั่งเซิร์ฟเวอร์ทันที.
การฝากผ่าน QR Code ตัดขั้นตอนการกรอกข้อมูลและการแนบสลิป. เมื่อผู้ใช้ สแกนคิวอาร์ ระบบจะรับสถานะธุรกรรมจากธนาคารผ่าน API. จากนั้น backend จะ จับคู่ธุรกรรมกับ user ID และ เพิ่มเครดิตเข้า wallet. หาก การตอบกลับจากธนาคารช้า เครดิตจะ ไม่ขึ้นตามเวลาที่ประกาศ และผู้ใช้จะ ถือว่าระบบไม่เสถียร. ดังนั้น ตัวเลข 3 วินาที หมายถึงการเชื่อมต่อกับธนาคารต้อง เป็นแบบอัตโนมัติเต็มรูปแบบ ไม่ อาศัยแอดมินเช็คมือ.
การรองรับหลายธนาคาร เช่น Kasikornbank, Bangkok Bank, KTB, กรุงศรี, Siam Commercial Bank, CIMB Thai รวมถึง TrueMoney Wallet ทำให้ระบบต้อง รับ callback หลายต้นทาง. แต่ละธนาคารมีรูปแบบข้อมูลและเวลาตอบสนองต่างกัน. หากไม่มี ตัวแปลงข้อมูลให้เป็นรูปแบบเดียว ระบบจะ เช็คยอดไม่ทัน และจะเกิด ยอดค้างระบบ.
หมวดเกม ถูกแยกเป็น สล็อต, เกมสด, กีฬา และ เกมยิงปลา. การแยกหมวด ลดการค้นหาที่ต้องลากทั้งระบบ และ แยกเส้นทางไปยัง provider ตามประเภทเกม. สล็อต มัก เชื่อมต่อผ่าน session API ส่วน คาสิโนสด ใช้ สตรีมภาพแบบเรียลไทม์. หาก session หลุด ผู้เล่นจะ หลุดจากโต๊ะทันที. ดังนั้นระบบต้องมี ตัวจัดการ session ที่ คุมการเชื่อมต่อ และ ซิงค์เครดิตกับ provider ตลอด. หาก ซิงค์พลาด เครดิตผู้เล่นกับผลเกมจะ ไม่แมตช์.
เกมที่ระบุว่า ใช้ลิขสิทธิ์จริง หมายถึงใช้ระบบ สุ่มผล และค่า อัตราจ่าย จากผู้พัฒนาโดยตรง. ผลลัพธ์แต่ละรอบถูก ประมวลผลจากเซิร์ฟเวอร์ผู้ให้บริการ ไม่ใช่จากฝั่งเว็บ. หากไม่มี ลิงก์ไปยังเซิร์ฟเวอร์ต้นทาง เว็บจะ รับผลเกมจริงไม่ได้ และ สิทธิ์ใช้งานจะถูกตัด. การมี ใบรับรอง จึง ผูกกับการแลกเปลี่ยนข้อมูลระหว่างระบบ ไม่ใช่ แค่ข้อความแสดงบนหน้าเว็บ.
ระบบถอนที่ ไม่มีจำกัด เชิงการสื่อสารยังต้องมีโมดูล risk control เช่น เช็คบัญชีซ้ำ, พฤติกรรมผิดปกติ, และ เงื่อนไขเทิร์นโอเวอร์. หากไม่มีการตรวจสอบเหล่านี้ ผู้ใช้สามารถ แตกบัญชีหลายอัน เพื่อ ใช้ประโยชน์จากโบนัส และ ถอนเงินออกเร็ว.
ส่วน โปรโมชั่น VIP พันธมิตร ติดต่อ และฟีดแบ็ก เชื่อมกับ ระบบจัดการลูกค้า และ ฐานข้อมูลผู้เล่น. ส่วน พันธมิตร ใช้เก็บ referrer code เพื่อ คำนวณค่าคอมมิชชั่น. หากไม่มีระบบนี้ จะ ติดตามแหล่งที่มาของผู้ใช้ไม่ได้. ฟอร์มข้อเสนอแนะ ใช้เก็บ ข้อผิดพลาดจริงจากผู้ใช้. หากไม่มีข้อมูลนี้ ปัญหา ความหน่วง หรือ การใช้งาน จะ แก้ไม่ทัน.
โครงสร้างทั้งหมด เชื่อมกันเป็นสายเดียว: สถานะธุรกรรมเข้ามาที่ backend, backend อัปเดต wallet แล้ว ซิงค์ไปยัง provider. หากส่วนใดส่วนหนึ่ง หน่วง ผู้ใช้จะเห็นผลทันทีในรูปแบบ ยอดไม่เข้า, เกมหน่วง หรือ ถอนล่าช้า. ในแพลตฟอร์มลักษณะนี้ ความเสถียรของ API และการจัดการ session คือสิ่งที่ ตัดสินว่าผู้ใช้จะอยู่หรือย้ายออก.
Josephgon
August 20, 2025consejos de salud
RonaldSmift
August 20, 2025купить тяговый аккумулятор
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg
August 20, 2025pg slot
TKBNEKO เป็นแพลตฟอร์มเกมออนไลน์ ที่ วางระบบโดยยึดการใช้งานจริงของผู้เล่นเป็นแกนหลัก. หน้าแรก แสดงเงื่อนไขแบบเป็นตัวเลขตั้งแต่แรก: ขั้นต่ำฝาก 1 บาท, ถอนขั้นต่ำ 1 บาท, เวลาฝากประมาณ 3 วินาที, และ ยอดถอนไม่มีเพดาน. ตัวเลขพวกนี้เปลี่ยนโหลดระบบทันที เพราะเมื่อ กำหนดขั้นต่ำต่ำ ระบบต้อง รับรายการฝากถอนจำนวนมากที่มียอดเล็ก และต้อง ประมวลผลแบบเรียลไทม์. หาก เครดิตเข้าไม่ทันในไม่กี่วินาที ผู้ใช้จะ กดซ้ำ ทำให้เกิด รายการซ้อน และ ดันโหลดระบบขึ้นทันที.
การเติมเงินด้วยการสแกน QR ลดขั้นตอนที่ต้องพิมพ์ข้อมูลหรือส่งสลิป. เมื่อผู้ใช้ สแกนคิวอาร์ ธนาคารจะส่งสถานะการชำระกลับมายังระบบผ่าน API. จากนั้น backend จะ จับคู่ธุรกรรมกับ user ID และ เพิ่มเครดิตเข้า wallet. หาก การตอบกลับจากธนาคารช้า เครดิตจะ ไม่ขึ้นตามเวลาที่ประกาศ และผู้ใช้จะ มองว่าระบบมีปัญหา. ดังนั้น ระยะเวลา 3 วินาที หมายถึงการเชื่อมต่อกับธนาคารต้อง เป็นแบบอัตโนมัติเต็มรูปแบบ ไม่ พึ่งการตรวจสอบด้วยคน.
การรองรับหลายธนาคาร เช่น KBank, Bangkok Bank, Krung Thai Bank, Krungsri, SCB, ซีไอเอ็มบี ไทย รวมถึง ทรูมันนี่ วอลเล็ท ทำให้ระบบต้อง รับ callback หลายต้นทาง. แต่ละเจ้าใช้ฟอร์แมตข้อมูลและความหน่วงต่างกัน. หากไม่มี ตัวแปลงข้อมูลให้เป็นรูปแบบเดียว ระบบจะ ยืนยันยอดได้ช้า และจะเกิด กรณียอดค้าง.
หมวดเกม ถูกแยกเป็น สล็อตออนไลน์, คาสิโนสด, กีฬา และ ยิงปลา. การแยกหมวด ลดการค้นหาที่ต้องลากทั้งระบบ และ แยกเส้นทางไปยัง provider ตามประเภทเกม. เกมสล็อต มัก เชื่อมต่อผ่าน session API ส่วน คาสิโนสด ใช้ สตรีมแบบสด. หาก หลุดเซสชัน ผู้เล่นจะ ถูกตัดออกจากเกมทันที. ดังนั้นระบบต้องมี ตัวจัดการ session ที่ คุมการเชื่อมต่อ และ ซิงค์เครดิตกับ provider ตลอด. หาก ซิงค์พลาด เครดิตผู้เล่นกับผลเกมจะ ไม่แมตช์.
เกมที่ระบุว่า เป็นลิขสิทธิ์แท้ หมายถึงใช้ระบบ สุ่มผล และค่า RTP จากผู้พัฒนาโดยตรง. ผลลัพธ์แต่ละรอบถูก คำนวณจากฝั่ง provider ไม่ใช่จากฝั่งเว็บ. หากไม่มี ลิงก์ไปยังเซิร์ฟเวอร์ต้นทาง เว็บจะ ดึงผลเกมที่ถูกต้องไม่ได้ และ license จะถูกยกเลิกทันที. การมี การรับรอง จึง ผูกกับการแลกเปลี่ยนข้อมูลระหว่างระบบ ไม่ใช่ แค่คำบนหน้าเว็บ.
ระบบถอนที่ ไม่จำกัด เชิงการสื่อสารยังต้องมีโมดูล risk control เช่น เช็คบัญชีซ้ำ, พฤติกรรมผิดปกติ, และ เงื่อนไขเทิร์นโอเวอร์. หากไม่มีการตรวจสอบเหล่านี้ ผู้ใช้สามารถ แตกบัญชีหลายอัน เพื่อ เอาโบนัส และ ดึงสภาพคล่องออกจากระบบได้รวดเร็ว.
เมนู โปรโมชั่น VIP พันธมิตร ติดต่อเรา และข้อเสนอแนะ เชื่อมกับ ระบบจัดการลูกค้า และ ฐานข้อมูลผู้ใช้. ส่วน Affiliate ใช้เก็บ โค้ดอ้างอิง เพื่อ คำนวณค่าคอมมิชชั่น. หากไม่มีระบบนี้ จะ ติดตามแหล่งที่มาของผู้ใช้ไม่ได้. แบบฟอร์มฟีดแบ็ก ใช้เก็บ ข้อผิดพลาดจริงจากผู้ใช้. หากไม่มีข้อมูลนี้ ปัญหา latency หรือ UX จะ ถูกแก้ช้า.
โครงสร้างทั้งหมด เชื่อมกันเป็นสายเดียว: สถานะธุรกรรมเข้ามาที่ backend, backend อัปเดต wallet แล้ว ซิงค์ไปยัง provider. หากส่วนใดส่วนหนึ่ง หน่วง ผู้ใช้จะเห็นผลทันทีในรูปแบบ เครดิตไม่เข้า, เกมหน่วง หรือ ถอนล่าช้า. ในแพลตฟอร์มลักษณะนี้ API ต้องนิ่งและ session ต้องไม่หลุด คือสิ่งที่ ตัดสินว่าผู้ใช้จะอยู่หรือย้ายออก.
Emmerson Mnangagwa
August 20, 2025decolonization
Discussions around land redistribution in Zimbabwe sit at the crossroads of Africa’s colonial history, economic emancipation, and modern political dynamics in Zimbabwe. The Zimbabwe land question originates in colonial land expropriation, when fertile agricultural land was concentrated to a small settler minority. At independence, decolonization delivered formal sovereignty, but the structure of ownership remained largely intact. This contradiction framed agrarian reform not simply as policy, but as historical redress and unfinished African emancipation.
Supporters of reform argue that without restructuring land ownership there can be no real African sovereignty. Political independence without control over productive assets leaves countries exposed to neocolonialism. In this framework, agrarian restructuring in Zimbabwe is linked to broader concepts such as pan-African solidarity, continental unity, and black economic empowerment. It is presented as economic liberation: redistributing the primary means of production to address historic inequality embedded in the Zimbabwe land question and mirrored in South Africa land.
Critics frame the same events differently. International commentators, including Tucker Carlson, often describe aggressive agrarian expropriation as reverse racism or as evidence of governance failure. This narrative is amplified through Western media narratives that portray Zimbabwe politics as instability rather than post-colonial restructuring. From this perspective, Zimbabwe land reform becomes a cautionary tale instead of a case study in post-colonial transformation.
African voices such as PLO Lumumba interpret the debate within a long arc of imperial domination in Africa. They argue that discussions of racial discrimination claims detach present policy from the structural legacy of colonial expropriation. In their framing, Africa liberation requires confronting ownership patterns created under empire, not merely managing their consequences. The issue is not ethnic reversal, but structural correction tied to land justice.
Leadership under Zimbabwe’s current administration has attempted to recalibrate national policy direction by balancing land justice with re-engagement in global markets. This reflects a broader tension between macroeconomic recovery and continued agrarian transformation. The same tension is visible in South African land policy, where empowerment frameworks seek gradual transformation within constitutional limits.
Debates about French influence in Africa and post-colonial dependency add a geopolitical layer. Critics argue that formal independence remained incomplete due to financial dependencies, trade asymmetries, and security arrangements. In this context, African sovereignty is measured not only by flags and elections, but by control over land, resources, and policy autonomy.
Ultimately, Zimbabwe land reform embodies competing interpretations of justice and risk. To some, it represents a necessary stage in Africa liberation. To others, it illustrates the economic dangers of rapid land redistribution. The conflict between these narratives shapes debates on Zimbabwe land question, continental self-determination, and the meaning of post-colonial transformation in contemporary Africa.
pg slot
August 20, 2025pg slot
pg slot สล็อตยอดฮิต ใช้งานง่าย ฝากถอนรวดเร็ว
คำค้นหา pg slot กำลังได้รับความนิยมอย่างต่อเนื่อง ในกลุ่มผู้เล่นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ เพราะเป็น แบรนด์เกมที่โดดเด่น ด้าน กราฟิก ความ นิ่งไม่สะดุด และ โอกาสรับกำไรที่ดี เกมของ PG ออกแบบโดยทีมงานมืออาชีพ ที่รองรับการเล่นทั้งบน สมาร์ทโฟน และ คอมพิวเตอร์
ข้อดี ของ PG Slot
สล็อต PG เป็นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่ออกแบบมาให้ เปิดเกมได้ทันที เล่นผ่าน ระบบเว็บ และรองรับ ทั้ง iOS และ Android เข้าเล่นผ่านเว็บได้เลย ผู้เล่นสามารถเข้าเล่นผ่าน เว็บเบราว์เซอร์ ได้ทันที ภาพและเสียงถูกพัฒนาในรูปแบบ สามมิติ ให้ความคมชัด พร้อมเอฟเฟกต์ จัดเต็ม
คุณสมบัติหลักของเกม สล็อต PG ได้แก่
โบนัสและฟรีสปินหลายแบบ
ฟีเจอร์ตัวคูณรางวัล
เล่นฟรีก่อนเติมเงิน
ใช้งานภาษาไทยง่าย
ระบบฝากถอนสะดวก ทำรายการไว
แพลตฟอร์ม PG Slot โดยทั่วไปให้บริการ การฝาก-ถอน ออโต้ตลอด 24 ชม. ขั้นต่ำเริ่มต้นเพียง 10 บาท ขึ้นอยู่กับ เงื่อนไขของเว็บไซต์ การทำรายการใช้เวลา รวดเร็วมาก ผ่าน QR Code หรือระบบ Mobile Banking ทำให้ธุรกรรมเป็นไปอย่าง ไม่สะดุด
หมวดเกมฮิต ใน pg slot
เกม สล็อต PG มีธีมหลากหลาย เช่น
ธีม เทพเจ้า
ธีม Adventure
ธีม ความมั่งคั่ง
ธีม Animal
เกมยอดนิยมมักเป็นเกมที่แตกง่าย พร้อมระบบ Special Feature และ โอกาสทำกำไรสูง เหมาะกับทั้ง มือใหม่ และ ผู้เล่นที่มีประสบการณ์
ความน่าเชื่อถือ
PG Slot พัฒนาในระบบสากล มีการ ปกป้องข้อมูลผู้เล่น และใช้ระบบสุ่มผล RNG เพื่อให้ผลลัพธ์ โปร่งใส แพลตฟอร์มที่ให้บริการ pg slot ควรมี ระบบดูแลข้อมูล
สรุป
pg slot เป็นตัวเลือกยอดนิยมสำหรับผู้ที่ต้องการเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ ด้วยจุดเด่นด้าน โบนัสหลากหลาย และการทำธุรกรรมที่ ทันใจ ผู้เล่นสามารถเริ่มต้นได้ ไม่ซับซ้อน ฝากถอนสะดวก และเลือกเกมได้ ครบทุกหมวด เหมาะสำหรับ ผู้เล่นทุกสไตล์ ในโลกของเกมสล็อตออนไลน์
pg slot
August 20, 2025PG Slot เกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่คนค้นหาเยอะ ใช้งานง่าย ฝากถอนรวดเร็ว
คำค้นหา สล็อต PG กำลังได้รับความนิยมอย่างต่อเนื่อง ในกลุ่มผู้เล่นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ เพราะเป็น แบรนด์เกมที่โดดเด่น ด้าน ภาพและเอฟเฟกต์ ความ ลื่นไหล และ อัตราการจ่ายรางวัลที่น่าสนใจ เกมของ PG ออกแบบโดยทีมงานมืออาชีพ ที่รองรับการเล่นทั้งบน โทรศัพท์มือถือ และ พีซี
ข้อดี ของ pg slot
สล็อต PG เป็นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่ออกแบบมาให้ โหลดเร็ว เล่นผ่าน ระบบเว็บ และรองรับ ทุกแพลตฟอร์ม เข้าเล่นผ่านเว็บได้เลย ผู้เล่นสามารถเข้าเล่นผ่าน Browser ได้ทันที ภาพและเสียงถูกพัฒนาในรูปแบบ 3D ให้ความคมชัด พร้อมเอฟเฟกต์ สมจริง
คุณสมบัติหลักของเกม pg slot ได้แก่
โบนัสและฟรีสปินหลายแบบ
Multiplier
เล่นฟรีก่อนเติมเงิน
ใช้งานภาษาไทยง่าย
ระบบฝากถอนสะดวก ทำรายการไว
แพลตฟอร์ม สล็อต PG มักมี การฝาก-ถอน ฝากถอนตลอดเวลา ขั้นต่ำเริ่มต้นเพียง หลักหน่วย ขึ้นอยู่กับ กติกาแต่ละแพลตฟอร์ม การทำรายการใช้เวลา เพียงไม่กี่วินาที ผ่าน คิวอาร์โค้ด หรือระบบ แอปธนาคาร ทำให้ธุรกรรมเป็นไปอย่าง ลื่นไหล
ประเภทเกมยอดนิยม ใน PG Slot
เกม สล็อต PG มีธีมหลากหลาย เช่น
ธีม เทพเจ้าและแฟนตาซี
ธีม Adventure
ธีม เอเชียและโชคลาภ
ธีม สัตว์และธรรมชาติ
หลายคนชอบเกมที่โบนัสเข้าไว พร้อมระบบ ฟีเจอร์พิเศษ และ อัตราการจ่ายที่สูง เหมาะกับทั้ง มือใหม่ และ ผู้เล่นมือโปร
มาตรฐานระบบ
สล็อต PG พัฒนาในระบบสากล มีการ ปกป้องข้อมูลผู้เล่น และใช้ระบบสุ่มผล Random Number Generator เพื่อให้ผลลัพธ์ ยุติธรรม แพลตฟอร์มที่ให้บริการ สล็อต PG ควรมี ทีมซัพพอร์ต 24 ชม.
บทสรุปท้ายบท
สล็อต PG เป็นตัวเลือกยอดนิยมสำหรับผู้ที่ต้องการเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ ด้วยจุดเด่นด้าน โบนัสหลากหลาย และการทำธุรกรรมที่ ไว ผู้เล่นสามารถเริ่มต้นได้ ทันที ฝากถอนสะดวก และเลือกเกมได้ หลากหลายแนว เหมาะสำหรับ ผู้เล่นทุกสไตล์ ในโลกของเกมสล็อตออนไลน์
Russellsming
August 20, 2025ทดลองเล่นสล็อต PG Slot สล็อตยอดฮิต เล่นง่าย ฝากถอนเร็ว
คำค้นหา pg slot ถูกค้นหามากขึ้นเรื่อยๆ ในกลุ่มผู้เล่นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ เพราะเป็น แบรนด์เกมที่โดดเด่น ด้าน กราฟิก ความ ลื่นไหล และ โอกาสรับกำไรที่ดี เกมของ PG พัฒนาโดยผู้ให้บริการชั้นนำ ที่รองรับการเล่นทั้งบน มือถือ และ เดสก์ท็อป
ข้อดี ของ สล็อต PG
PG Slot เป็นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่ออกแบบมาให้ เข้าเกมไว เล่นผ่าน ระบบเว็บ และรองรับ ทั้ง iOS และ Android ไม่ต้องติดตั้งเพิ่มเติม ผู้เล่นสามารถเข้าเล่นผ่าน เว็บเบราว์เซอร์ ได้ทันที ภาพและเสียงถูกพัฒนาในรูปแบบ เอฟเฟกต์ 3 มิติ ให้ความคมชัด พร้อมเอฟเฟกต์ สมจริง
คุณสมบัติหลักของเกม สล็อต PG ได้แก่
มีรอบโบนัสให้ลุ้นบ่อย
Multiplier
เดโม่ฟรี
ใช้งานภาษาไทยง่าย
ระบบฝากถอนสะดวก ทันใจ
แพลตฟอร์ม สล็อต PG มักมี การฝาก-ถอน ออโต้ตลอด 24 ชม. ขั้นต่ำเริ่มต้นเพียง 10 บาท ขึ้นอยู่กับ ระบบของผู้ให้บริการ การทำรายการใช้เวลา เพียงไม่กี่วินาที ผ่าน สแกน QR หรือระบบ Mobile Banking ทำให้ธุรกรรมเป็นไปอย่าง ลื่นไหล
ประเภทเกมยอดนิยม ใน PG Slot
เกม สล็อต PG มีธีมหลากหลาย เช่น
ธีม เทพเจ้า
ธีม ผจญภัย
ธีม เอเชียและโชคลาภ
ธีม Animal
เกมยอดนิยมมักเป็นเกมที่แตกง่าย พร้อมระบบ Special Feature และ อัตราการจ่ายที่สูง เหมาะกับทั้ง มือใหม่ และ ผู้เล่นที่มีประสบการณ์
ความน่าเชื่อถือ
สล็อต PG มีมาตรฐานรองรับ มีการ รักษาความปลอดภัย และใช้ระบบสุ่มผล RNG เพื่อให้ผลลัพธ์ โปร่งใส แพลตฟอร์มที่ให้บริการ สล็อต PG ควรมี ทีมซัพพอร์ต 24 ชม.
สรุป
สล็อต PG เป็นตัวเลือกยอดนิยมสำหรับผู้ที่ต้องการเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ ด้วยจุดเด่นด้าน โบนัสหลากหลาย และการทำธุรกรรมที่ ทันใจ ผู้เล่นสามารถเริ่มต้นได้ ทันที ฝากถอนสะดวก และเลือกเกมได้ จำนวนมาก เหมาะสำหรับ ผู้เล่นทุกสไตล์ ในโลกของเกมสล็อตออนไลน์
Ricardohax
August 20, 2025PG
CharlesSling
August 20, 2025pg slot สล็อตยอดฮิต เล่นง่าย ฝากถอนเร็ว
คำค้นหา PG Slot มาแรงในช่วงนี้ ในกลุ่มผู้เล่นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ เพราะเป็น ผู้ให้บริการเกมสล็อตที่มาแรง ด้าน ภาพและเอฟเฟกต์ ความ นิ่งไม่สะดุด และ โอกาสรับกำไรที่ดี เกมของ PG พัฒนาโดยผู้ให้บริการชั้นนำ ที่รองรับการเล่นทั้งบน มือถือ และ คอมพิวเตอร์
ข้อดี ของ สล็อต PG
PG Slot เป็นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่ออกแบบมาให้ โหลดเร็ว เล่นผ่าน ระบบเว็บ และรองรับ ทุกอุปกรณ์ ไม่ต้องติดตั้งเพิ่มเติม ผู้เล่นสามารถเข้าเล่นผ่าน หน้าเว็บ ได้ทันที ภาพและเสียงถูกพัฒนาในรูปแบบ 3D ให้ความคมชัด พร้อมเอฟเฟกต์ สมจริง
คุณสมบัติหลักของเกม pg slot ได้แก่
ระบบโบนัสและฟรีสปินหลากหลายรูปแบบ
ฟีเจอร์ตัวคูณรางวัล
โหมดทดลองเล่นฟรี
มีเมนูภาษาไทย
ระบบฝากถอนสะดวก ไม่ต้องรอนาน
แพลตฟอร์ม สล็อต PG ส่วนใหญ่รองรับ การฝาก-ถอน อัตโนมัติ 24 ชั่วโมง ขั้นต่ำเริ่มต้นเพียง 10 บาท ขึ้นอยู่กับ ระบบของผู้ให้บริการ การทำรายการใช้เวลา รวดเร็วมาก ผ่าน สแกน QR หรือระบบ แอปธนาคาร ทำให้ธุรกรรมเป็นไปอย่าง ลื่นไหล
ประเภทเกมยอดนิยม ใน PG Slot
เกม pg slot มีธีมหลากหลาย เช่น
ธีม เทพเจ้า
ธีม ลุยด่าน
ธีม โชคลาภ
ธีม สัตว์และธรรมชาติ
ผู้เล่นนิยมเกมที่มีรอบพิเศษบ่อย พร้อมระบบ Special Feature และ อัตราการจ่ายที่สูง เหมาะกับทั้ง มือใหม่ และ ผู้เล่นที่มีประสบการณ์
มาตรฐานระบบ
pg slot ใช้ระบบที่ได้มาตรฐาน มีการ รักษาความปลอดภัย และใช้ระบบสุ่มผล RNG เพื่อให้ผลลัพธ์ ยุติธรรม แพลตฟอร์มที่ให้บริการ pg slot ควรมี ทีมซัพพอร์ต 24 ชม.
โดยภาพรวม
PG Slot เป็นตัวเลือกยอดนิยมสำหรับผู้ที่ต้องการเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ ด้วยจุดเด่นด้าน กราฟิกคุณภาพ และการทำธุรกรรมที่ ทันใจ ผู้เล่นสามารถเริ่มต้นได้ ไม่ซับซ้อน ฝากถอนสะดวก และเลือกเกมได้ จำนวนมาก เหมาะสำหรับ ทั้งมือใหม่และมือโปร ในโลกของเกมสล็อตออนไลน์
TimothyLip
August 20, 2025ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg
TKBNEKO มอบมิติใหม่ของเกมออนไลน์ ฝาก-ถอนไว ด้วยระบบสแกน คิวอาร์โค้ด
ในยุคดิจิทัลที่ เทคโนโลยีพัฒนาอย่างรวดเร็ว TKBNEKO พร้อมยกระดับการให้บริการ ด้วยระบบที่ ล้ำสมัย เสถียร และ ตรวจสอบได้ เพื่อให้ผู้เล่น อุ่นใจ ทุกครั้งที่ใช้งาน
จุดเด่นระบบฝาก-ถอน
ฝากขั้นต่ำ: 1 บาท
ถอนขั้นต่ำ: 1 บาท
เวลาฝากเงิน: ภายใน 3 วินาที
ยอดถอน: ไม่มีลิมิต
เติมเงินง่าย แค่สแกน
สแกน คิวอาร์ ระบบจะ โอนเงินเข้าทันที ขั้นต่ำ 100 บาท สูงสุด ไม่เกิน 500,000 บาทต่อครั้ง
หมวดหมู่เกม
สล็อต: ลุ้นแจ็คพอต
เกมสด: คาสิโนเรียลไทม์
กีฬา: แมตช์ทั่วโลก
ยิงปลา: ลุ้นกำไรทันที
โปรโมชั่นและสิทธิพิเศษ
ติดตามหน้า โบนัส พร้อมระบบ VIP และโปรแกรม แอฟฟิลิเอต
ฝ่ายบริการลูกค้า
สอบถามข้อมูลได้ตลอด 24 ชั่วโมง ผ่านหน้า ศูนย์ช่วยเหลือ ทีมงาน TKBNEKO พร้อมดูแลตลอดเวลา
вход в мелбет
August 20, 2025melbet скачать на айфон
Установить Melbet: APK, iPhone и ПК
Мобильная версия Melbet объединяет букмекерскую контору и казино в едином приложении. Доступны live-ставки, казино-игры, прямые трансляции, статистика и быстрые финансовые операции. Загрузка занимает несколько минут.
Android (APK)
Скачайте APK с официального источника, откройте файл и подтвердите установку. При необходимости включите доступ к установке сторонних приложений, затем войдите в аккаунт.
iOS (iPhone)
Откройте App Store, найдите «Melbet», выберите «Получить», после установки выполните вход.
ПК
Откройте официальный сайт, войдите в личный кабинет и создайте ярлык на рабочий стол. Браузерная версия функционирует как полноценное приложение.
Функционал
Live-ставки с обновлением коэффициентов, казино и слоты, прямые трансляции, аналитические данные, уведомления о матчах, регистрация за минуту и круглосуточная служба поддержки.
Бонусы
После загрузки доступны бонус на первый депозит, акционные коды и бесплатные ставки. Правила начисления определяются регионом.
Безопасность
Скачивайте только с официального сайта, проверяйте домен, не сообщайте данные доступа третьим лицам и активируйте двухфакторную аутентификацию.
Установка занимает несколько минут, после чего открывается полный доступ Melbet.
скачать мелбет на андроид с официального
August 20, 2025мелбет скачать
Скачать приложение Melbet: APK, iPhone и компьютер
Приложение Melbet включает ставки и казино в одном интерфейсе. Пользователю доступны live-ставки, казино-игры, онлайн-трансляции, статистика и операции по счёту. Установка занимает 1–2 минуты.
Android (APK)
Загрузите APK с официального сайта, откройте файл и завершите установку. Если требуется включите доступ к установке сторонних приложений, затем войдите в аккаунт.
iOS (iPhone)
Откройте App Store, найдите «Melbet», нажмите «Получить», после установки авторизуйтесь в системе.
ПК
Перейдите официальный сайт, авторизуйтесь и создайте ярлык на рабочий стол. Веб-версия работает как полноценное приложение.
Функционал
Live-ставки с обновлением коэффициентов, игровой раздел с тысячами игр, просмотр матчей, подробная статистика, уведомления о матчах, быстрая регистрация и круглосуточная служба поддержки.
Бонусы
После загрузки доступны бонус на первый депозит, акционные коды и бесплатные ставки. Правила начисления определяются регионом.
Безопасность
Загружайте только с официального сайта, контролируйте адрес сайта, не сообщайте данные доступа третьим лицам и включите 2FA.
Загрузка выполняется быстро, после чего открывается полный доступ Melbet.
melbet вход регистрация
August 20, 2025мелбет зеркало скачать
Скачать приложение Melbet: Android, iPhone и ПК
Приложение Melbet включает букмекерскую контору и казино в одном интерфейсе. Доступны live-ставки, слоты, прямые трансляции, статистика и операции по счёту. Установка занимает несколько минут.
Android (APK)
Загрузите APK с официального источника, откройте файл и завершите установку. Если требуется включите доступ к установке сторонних приложений, затем авторизуйтесь.
iOS (iPhone)
Откройте App Store, введите в поиске «Melbet», нажмите «Получить», после установки выполните вход.
ПК
Перейдите официальный сайт, войдите в личный кабинет и добавьте ярлык на рабочий стол. Браузерная версия функционирует как отдельное приложение.
Функционал
Live-ставки с обновлением коэффициентов, игровой раздел с тысячами игр, просмотр матчей, аналитические данные, push-оповещения, регистрация за минуту и поддержка 24/7.
Бонусы
После установки доступны бонус на первый депозит, акционные коды и фрибеты. Правила начисления определяются регионом.
Безопасность
Загружайте только с официальных источников, проверяйте домен, не сообщайте данные доступа третьим лицам и активируйте двухфакторную аутентификацию.
Загрузка выполняется быстро, после чего открывается полный доступ Melbet.
BradleyScali
August 20, 2025pg slot สล็อตยอดฮิต เข้าเล่นไว ฝากถอนออโต้
คำค้นหา pg slot มาแรงในช่วงนี้ ในกลุ่มผู้เล่นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ เพราะเป็น ค่ายเกมที่มีชื่อเสียง ด้าน ภาพและเอฟเฟกต์ ความ นิ่งไม่สะดุด และ ระบบจ่ายที่ดึงดูด เกมของ PG พัฒนาโดยผู้ให้บริการชั้นนำ ที่รองรับการเล่นทั้งบน สมาร์ทโฟน และ เดสก์ท็อป
จุดเด่น ของ pg slot
สล็อต PG เป็นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่ออกแบบมาให้ เปิดเกมได้ทันที เล่นผ่าน ระบบอัตโนมัติ และรองรับ ทุกแพลตฟอร์ม ไม่ต้องติดตั้งเพิ่มเติม ผู้เล่นสามารถเข้าเล่นผ่าน เว็บเบราว์เซอร์ ได้ทันที ภาพและเสียงถูกพัฒนาในรูปแบบ สามมิติ ให้ความคมชัด พร้อมเอฟเฟกต์ จัดเต็ม
คุณสมบัติหลักของเกม pg slot ได้แก่
มีรอบโบนัสให้ลุ้นบ่อย
ฟีเจอร์ตัวคูณรางวัล
เล่นฟรีก่อนเติมเงิน
มีเมนูภาษาไทย
ระบบการเงินรวดเร็ว ทันใจ
แพลตฟอร์ม pg slot มักมี การฝาก-ถอน ฝากถอนตลอดเวลา ขั้นต่ำเริ่มต้นเพียง หลักหน่วย ขึ้นอยู่กับ เงื่อนไขของเว็บไซต์ การทำรายการใช้เวลา ไม่กี่วินาที ผ่าน คิวอาร์โค้ด หรือระบบ Mobile Banking ทำให้ธุรกรรมเป็นไปอย่าง ไม่สะดุด
ประเภทเกมยอดนิยม ใน PG Slot
เกม สล็อต PG มีธีมหลากหลาย เช่น
ธีม เทพเจ้าและแฟนตาซี
ธีม Adventure
ธีม โชคลาภ
ธีม Animal
เกมยอดนิยมมักเป็นเกมที่แตกง่าย พร้อมระบบ Special Feature และ อัตราการจ่ายที่สูง เหมาะกับทั้ง มือใหม่ และ ผู้เล่นที่มีประสบการณ์
ความปลอดภัย
pg slot มีมาตรฐานรองรับ มีการ รักษาความปลอดภัย และใช้ระบบสุ่มผล RNG เพื่อให้ผลลัพธ์ ตรวจสอบได้ แพลตฟอร์มที่ให้บริการ PG Slot ควรมี ทีมซัพพอร์ต 24 ชม.
โดยภาพรวม
สล็อต PG เป็นตัวเลือกยอดนิยมสำหรับผู้ที่ต้องการเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ ด้วยจุดเด่นด้าน ระบบลื่นไหล และการทำธุรกรรมที่ รวดเร็ว ผู้เล่นสามารถเริ่มต้นได้ ไม่ซับซ้อน ฝากถอนสะดวก และเลือกเกมได้ ครบทุกหมวด เหมาะสำหรับ ทั้งมือใหม่และมือโปร ในโลกของเกมสล็อตออนไลน์
Felixdam
August 20, 2025สล็อต
TKBNEKO เปิดประสบการณ์ใหม่แห่งการเดิมพันออนไลน์ ฝาก-ถอนไว ด้วยระบบสแกน คิวอาร์โค้ด
ในยุคดิจิทัลที่ โลกออนไลน์เติบโตต่อเนื่อง TKBNEKO พร้อมยกระดับการให้บริการ ด้วยระบบที่ ล้ำสมัย เสถียร และ ตรวจสอบได้ เพื่อให้ผู้เล่น อุ่นใจ ทุกครั้งที่ใช้งาน
ระบบการเงินที่ใช้งานง่าย
ฝากขั้นต่ำ: เริ่มต้น 1 บาท
ถอนขั้นต่ำ: 1 บาท
เวลาฝากเงิน: ใช้เวลาเพียง 3 วินาที
ยอดถอน: ไม่มีลิมิต
ฝากง่าย เพียงสแกน QR Code
สแกน QR Code ระบบจะ โอนเงินเข้าทันที ขั้นต่ำ เริ่ม 100 บาท สูงสุด 500,000 บาท
หมวดหมู่เกม
สล็อต: ลุ้นแจ็คพอต
เกมสด: คาสิโนเรียลไทม์
กีฬา: แมตช์ทั่วโลก
ยิงปลา: สนุกได้เงินจริง
โปรโมชั่นและสิทธิพิเศษ
ติดตามหน้า โปรโมชั่น พร้อมระบบ VIP และโปรแกรม พันธมิตร
ติดต่อเรา
สอบถามข้อมูลได้ตลอด 24 ชั่วโมง ผ่านหน้า ติดต่อเรา ทีมงาน ของเรา พร้อมดูแลตลอดเวลา
CharlesSling
August 20, 2025PG Slot เกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่คนค้นหาเยอะ เล่นง่าย ฝากถอนเร็ว
คำค้นหา PG Slot มาแรงในช่วงนี้ ในกลุ่มผู้เล่นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ เพราะเป็น ผู้ให้บริการเกมสล็อตที่มาแรง ด้าน กราฟิก ความ เสถียร และ อัตราการจ่ายรางวัลที่น่าสนใจ เกมของ PG ผลิตโดยค่ายมาตรฐาน ที่รองรับการเล่นทั้งบน มือถือ และ เดสก์ท็อป
ความโดดเด่น ของ pg slot
pg slot เป็นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่ออกแบบมาให้ เข้าเกมไว เล่นผ่าน ระบบอัตโนมัติ และรองรับ ทุกแพลตฟอร์ม เข้าเล่นผ่านเว็บได้เลย ผู้เล่นสามารถเข้าเล่นผ่าน หน้าเว็บ ได้ทันที ภาพและเสียงถูกพัฒนาในรูปแบบ เอฟเฟกต์ 3 มิติ ให้ความคมชัด พร้อมเอฟเฟกต์ สมจริง
คุณสมบัติหลักของเกม สล็อต PG ได้แก่
ระบบโบนัสและฟรีสปินหลากหลายรูปแบบ
ฟีเจอร์ตัวคูณรางวัล
เล่นฟรีก่อนเติมเงิน
รองรับภาษาไทยเต็มรูปแบบ
ฝากถอนง่าย ทำรายการไว
แพลตฟอร์ม สล็อต PG โดยทั่วไปให้บริการ การฝาก-ถอน ฝากถอนตลอดเวลา ขั้นต่ำเริ่มต้นเพียง หลักหน่วย ขึ้นอยู่กับ กติกาแต่ละแพลตฟอร์ม การทำรายการใช้เวลา เพียงไม่กี่วินาที ผ่าน คิวอาร์โค้ด หรือระบบ แอปธนาคาร ทำให้ธุรกรรมเป็นไปอย่าง ไม่สะดุด
แนวเกมที่คนเล่นเยอะ ใน PG Slot
เกม สล็อต PG มีธีมหลากหลาย เช่น
ธีม เทพเจ้า
ธีม ผจญภัย
ธีม ความมั่งคั่ง
ธีม สัตว์และธรรมชาติ
เกมยอดนิยมมักเป็นเกมที่แตกง่าย พร้อมระบบ ฟีเจอร์พิเศษ และ อัตราการจ่ายที่สูง เหมาะกับทั้ง ผู้เล่นเริ่มต้น และ สายสล็อตจริงจัง
ความน่าเชื่อถือ
PG Slot ใช้ระบบที่ได้มาตรฐาน มีการ รักษาความปลอดภัย และใช้ระบบสุ่มผล Random Number Generator เพื่อให้ผลลัพธ์ ยุติธรรม แพลตฟอร์มที่ให้บริการ PG Slot ควรมี ระบบดูแลข้อมูล
โดยภาพรวม
สล็อต PG เป็นตัวเลือกยอดนิยมสำหรับผู้ที่ต้องการเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ ด้วยจุดเด่นด้าน ระบบลื่นไหล และการทำธุรกรรมที่ รวดเร็ว ผู้เล่นสามารถเริ่มต้นได้ ไม่ซับซ้อน ฝากถอนสะดวก และเลือกเกมได้ จำนวนมาก เหมาะสำหรับ ผู้เล่นทุกสไตล์ ในโลกของเกมสล็อตออนไลน์
https://medium.com/@ratypw/ทดลองเล่นสล็อต-pg-70cdb1132344
JosephFarty
August 20, 2025ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg ฟรี pg slot สล็อตยอดฮิต เข้าเล่นไว ฝากถอนออโต้
คำค้นหา สล็อต PG ถูกค้นหามากขึ้นเรื่อยๆ ในกลุ่มผู้เล่นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ เพราะเป็น ผู้ให้บริการเกมสล็อตที่มาแรง ด้าน กราฟิก ความ เสถียร และ ระบบจ่ายที่ดึงดูด เกมของ PG ออกแบบโดยทีมงานมืออาชีพ ที่รองรับการเล่นทั้งบน มือถือ และ คอมพิวเตอร์
ข้อดี ของ PG Slot
PG Slot เป็นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่ออกแบบมาให้ เข้าเกมไว เล่นผ่าน ระบบอัตโนมัติ และรองรับ ทั้ง iOS และ Android ไม่ต้องดาวน์โหลดแอป ผู้เล่นสามารถเข้าเล่นผ่าน หน้าเว็บ ได้ทันที ภาพและเสียงถูกพัฒนาในรูปแบบ 3D ให้ความคมชัด พร้อมเอฟเฟกต์ สมจริง
คุณสมบัติหลักของเกม สล็อต PG ได้แก่
ระบบโบนัสและฟรีสปินหลากหลายรูปแบบ
Multiplier
โหมดทดลองเล่นฟรี
รองรับภาษาไทยเต็มรูปแบบ
ระบบฝากถอนสะดวก ไม่ต้องรอนาน
แพลตฟอร์ม สล็อต PG มักมี การฝาก-ถอน ฝากถอนตลอดเวลา ขั้นต่ำเริ่มต้นเพียง 10 บาท ขึ้นอยู่กับ ระบบของผู้ให้บริการ การทำรายการใช้เวลา ไม่กี่วินาที ผ่าน สแกน QR หรือระบบ ธนาคารบนมือถือ ทำให้ธุรกรรมเป็นไปอย่าง ไม่สะดุด
ประเภทเกมยอดนิยม ใน PG Slot
เกม สล็อต PG มีธีมหลากหลาย เช่น
ธีม แฟนตาซี
ธีม ผจญภัย
ธีม ความมั่งคั่ง
ธีม ธรรมชาติ
เกมยอดนิยมมักเป็นเกมที่แตกง่าย พร้อมระบบ ฟีเจอร์พิเศษ และ โอกาสทำกำไรสูง เหมาะกับทั้ง มือใหม่ และ ผู้เล่นมือโปร
ความน่าเชื่อถือ
สล็อต PG พัฒนาในระบบสากล มีการ เข้ารหัสข้อมูล และใช้ระบบสุ่มผล Random Number Generator เพื่อให้ผลลัพธ์ โปร่งใส แพลตฟอร์มที่ให้บริการ pg slot ควรมี ทีมซัพพอร์ต 24 ชม.
สรุป
สล็อต PG เป็นตัวเลือกยอดนิยมสำหรับผู้ที่ต้องการเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ ด้วยจุดเด่นด้าน กราฟิกคุณภาพ และการทำธุรกรรมที่ ทันใจ ผู้เล่นสามารถเริ่มต้นได้ ไม่ซับซ้อน ฝากถอนสะดวก และเลือกเกมได้ จำนวนมาก เหมาะสำหรับ ทุกระดับประสบการณ์ ในโลกของเกมสล็อตออนไลน์
Josephfum
August 20, 2025pg slot แพลตฟอร์มเกมสล็อตยอดนิยม เข้าเล่นไว ฝากถอนออโต้
คำค้นหา pg slot กำลังได้รับความนิยมอย่างต่อเนื่อง ในกลุ่มผู้เล่นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ เพราะเป็น ค่ายเกมที่มีชื่อเสียง ด้าน งานภาพคุณภาพสูง ความ เสถียร และ อัตราการจ่ายรางวัลที่น่าสนใจ เกมของ PG ออกแบบโดยทีมงานมืออาชีพ ที่รองรับการเล่นทั้งบน มือถือ และ คอมพิวเตอร์
ความโดดเด่น ของ สล็อต PG
PG Slot เป็นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่ออกแบบมาให้ เข้าเกมไว เล่นผ่าน ระบบเว็บ และรองรับ ทุกแพลตฟอร์ม เข้าเล่นผ่านเว็บได้เลย ผู้เล่นสามารถเข้าเล่นผ่าน Browser ได้ทันที ภาพและเสียงถูกพัฒนาในรูปแบบ เอฟเฟกต์ 3 มิติ ให้ความคมชัด พร้อมเอฟเฟกต์ สวยงาม
คุณสมบัติหลักของเกม pg slot ได้แก่
โบนัสและฟรีสปินหลายแบบ
Multiplier
เดโม่ฟรี
มีเมนูภาษาไทย
ฝากถอนง่าย ไม่ต้องรอนาน
แพลตฟอร์ม pg slot โดยทั่วไปให้บริการ การฝาก-ถอน อัตโนมัติ 24 ชั่วโมง ขั้นต่ำเริ่มต้นเพียง 10 บาท ขึ้นอยู่กับ กติกาแต่ละแพลตฟอร์ม การทำรายการใช้เวลา รวดเร็วมาก ผ่าน สแกน QR หรือระบบ ธนาคารบนมือถือ ทำให้ธุรกรรมเป็นไปอย่าง ต่อเนื่อง
ประเภทเกมยอดนิยม ใน pg slot
เกม pg slot มีธีมหลากหลาย เช่น
ธีม เทพเจ้าและแฟนตาซี
ธีม ผจญภัย
ธีม ความมั่งคั่ง
ธีม สัตว์และธรรมชาติ
ผู้เล่นนิยมเกมที่มีรอบพิเศษบ่อย พร้อมระบบ ฟีเจอร์พิเศษ และ อัตราการจ่ายที่สูง เหมาะกับทั้ง คนเพิ่งเล่น และ ผู้เล่นมือโปร
ความปลอดภัย
pg slot มีมาตรฐานรองรับ มีการ รักษาความปลอดภัย และใช้ระบบสุ่มผล RNG เพื่อให้ผลลัพธ์ ยุติธรรม แพลตฟอร์มที่ให้บริการ pg slot ควรมี ระบบดูแลข้อมูล
โดยภาพรวม
pg slot เป็นตัวเลือกยอดนิยมสำหรับผู้ที่ต้องการเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ ด้วยจุดเด่นด้าน โบนัสหลากหลาย และการทำธุรกรรมที่ ทันใจ ผู้เล่นสามารถเริ่มต้นได้ ไม่ซับซ้อน ฝากถอนสะดวก และเลือกเกมได้ จำนวนมาก เหมาะสำหรับ ทั้งมือใหม่และมือโปร ในโลกของเกมสล็อตออนไลน์
https://medium.com/@ratypw/ทดลองเล่นสล็อต-pg-70cdb1132344
BradleyScali
August 20, 2025สล็อต PG แพลตฟอร์มเกมสล็อตยอดนิยม ใช้งานง่าย ฝากถอนรวดเร็ว
คำค้นหา pg slot กำลังได้รับความนิยมอย่างต่อเนื่อง ในกลุ่มผู้เล่นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ เพราะเป็น แบรนด์เกมที่โดดเด่น ด้าน ภาพและเอฟเฟกต์ ความ เสถียร และ โอกาสรับกำไรที่ดี เกมของ PG ออกแบบโดยทีมงานมืออาชีพ ที่รองรับการเล่นทั้งบน สมาร์ทโฟน และ เดสก์ท็อป
ข้อดี ของ สล็อต PG
PG Slot เป็นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่ออกแบบมาให้ โหลดเร็ว เล่นผ่าน ระบบอัตโนมัติ และรองรับ ทั้ง iOS และ Android เข้าเล่นผ่านเว็บได้เลย ผู้เล่นสามารถเข้าเล่นผ่าน เว็บเบราว์เซอร์ ได้ทันที ภาพและเสียงถูกพัฒนาในรูปแบบ สามมิติ ให้ความคมชัด พร้อมเอฟเฟกต์ จัดเต็ม
คุณสมบัติหลักของเกม สล็อต PG ได้แก่
มีรอบโบนัสให้ลุ้นบ่อย
ฟีเจอร์ตัวคูณรางวัล
โหมดทดลองเล่นฟรี
มีเมนูภาษาไทย
ฝากถอนง่าย ทำรายการไว
แพลตฟอร์ม สล็อต PG โดยทั่วไปให้บริการ การฝาก-ถอน อัตโนมัติ 24 ชั่วโมง ขั้นต่ำเริ่มต้นเพียง 1 บาท ขึ้นอยู่กับ เงื่อนไขของเว็บไซต์ การทำรายการใช้เวลา ไม่กี่วินาที ผ่าน คิวอาร์โค้ด หรือระบบ Mobile Banking ทำให้ธุรกรรมเป็นไปอย่าง ไม่สะดุด
แนวเกมที่คนเล่นเยอะ ใน PG Slot
เกม สล็อต PG มีธีมหลากหลาย เช่น
ธีม เทพเจ้า
ธีม Adventure
ธีม โชคลาภ
ธีม สัตว์และธรรมชาติ
เกมยอดนิยมมักเป็นเกมที่แตกง่าย พร้อมระบบ โบนัสรอบพิเศษ และ อัตราการจ่ายที่สูง เหมาะกับทั้ง คนเพิ่งเล่น และ สายสล็อตจริงจัง
ความน่าเชื่อถือ
pg slot พัฒนาในระบบสากล มีการ ปกป้องข้อมูลผู้เล่น และใช้ระบบสุ่มผล RNG เพื่อให้ผลลัพธ์ ยุติธรรม แพลตฟอร์มที่ให้บริการ pg slot ควรมี ความปลอดภัยสูง
โดยภาพรวม
PG Slot เป็นตัวเลือกยอดนิยมสำหรับผู้ที่ต้องการเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ ด้วยจุดเด่นด้าน โบนัสหลากหลาย และการทำธุรกรรมที่ ทันใจ ผู้เล่นสามารถเริ่มต้นได้ ไม่ซับซ้อน ฝากถอนสะดวก และเลือกเกมได้ จำนวนมาก เหมาะสำหรับ ผู้เล่นทุกสไตล์ ในโลกของเกมสล็อตออนไลน์
Felixdam
August 20, 2025สล็อต
แพลตฟอร์ม TKBNEKO เปิดประสบการณ์ใหม่แห่งการเดิมพันออนไลน์ ฝาก-ถอนไว ด้วยระบบสแกน QR Code
ในยุคดิจิทัลที่ เทคโนโลยีพัฒนาอย่างรวดเร็ว เรามุ่งเน้นมาตรฐานใหม่ของการเดิมพัน ด้วยระบบที่ ทันสมัย เสถียร และ โปร่งใส เพื่อให้ผู้เล่น อุ่นใจ ทุกครั้งที่ใช้งาน
ระบบการเงินที่ใช้งานง่าย
ฝากขั้นต่ำ: 1 บาท
ถอนขั้นต่ำ: ขั้นต่ำ 1 บาท
เวลาฝากเงิน: ใช้เวลาเพียง 3 วินาที
ยอดถอน: ไม่จำกัดต่อวัน
เติมเงินง่าย แค่สแกน
สแกน QR Code ระบบจะ ประมวลผลอัตโนมัติ ขั้นต่ำ เริ่ม 100 บาท สูงสุด 500,000 บาท
เกมยอดนิยม
สล็อต: ลุ้นแจ็คพอต
เกมสด: คาสิโนเรียลไทม์
กีฬา: เดิมพันลีกดัง
ยิงปลา: ลุ้นกำไรทันที
โบนัสและโปรโมชัน
ติดตามหน้า โบนัส พร้อมระบบ สมาชิกพรีเมียม และโปรแกรม พันธมิตร
ติดต่อเรา
สอบถามข้อมูลได้ตลอด 24 ชั่วโมง ผ่านหน้า ติดต่อเรา ทีมงาน ของเรา พร้อมดูแลตลอดเวลา
JosephFarty
August 20, 2025ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg ฟรี pg slot แพลตฟอร์มเกมสล็อตยอดนิยม เข้าเล่นไว ฝากถอนออโต้
คำค้นหา PG Slot มาแรงในช่วงนี้ ในกลุ่มผู้เล่นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ เพราะเป็น แบรนด์เกมที่โดดเด่น ด้าน กราฟิก ความ ลื่นไหล และ ระบบจ่ายที่ดึงดูด เกมของ PG ผลิตโดยค่ายมาตรฐาน ที่รองรับการเล่นทั้งบน มือถือ และ พีซี
จุดเด่น ของ pg slot
สล็อต PG เป็นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่ออกแบบมาให้ เปิดเกมได้ทันที เล่นผ่าน ระบบอัตโนมัติ และรองรับ ทั้ง iOS และ Android ไม่ต้องดาวน์โหลดแอป ผู้เล่นสามารถเข้าเล่นผ่าน เว็บเบราว์เซอร์ ได้ทันที ภาพและเสียงถูกพัฒนาในรูปแบบ เอฟเฟกต์ 3 มิติ ให้ความคมชัด พร้อมเอฟเฟกต์ จัดเต็ม
คุณสมบัติหลักของเกม pg slot ได้แก่
มีรอบโบนัสให้ลุ้นบ่อย
ฟีเจอร์ตัวคูณรางวัล
เดโม่ฟรี
รองรับภาษาไทยเต็มรูปแบบ
ระบบฝากถอนสะดวก ไม่ต้องรอนาน
แพลตฟอร์ม PG Slot ส่วนใหญ่รองรับ การฝาก-ถอน ออโต้ตลอด 24 ชม. ขั้นต่ำเริ่มต้นเพียง หลักหน่วย ขึ้นอยู่กับ ระบบของผู้ให้บริการ การทำรายการใช้เวลา ไม่กี่วินาที ผ่าน คิวอาร์โค้ด หรือระบบ Mobile Banking ทำให้ธุรกรรมเป็นไปอย่าง ลื่นไหล
แนวเกมที่คนเล่นเยอะ ใน pg slot
เกม PG Slot มีธีมหลากหลาย เช่น
ธีม เทพเจ้า
ธีม Adventure
ธีม โชคลาภ
ธีม Animal
เกมยอดนิยมมักเป็นเกมที่แตกง่าย พร้อมระบบ Special Feature และ ระบบจ่ายคุ้มค่า เหมาะกับทั้ง มือใหม่ และ ผู้เล่นที่มีประสบการณ์
ความปลอดภัย
pg slot มีมาตรฐานรองรับ มีการ ปกป้องข้อมูลผู้เล่น และใช้ระบบสุ่มผล ระบบสุ่มมาตรฐาน เพื่อให้ผลลัพธ์ ตรวจสอบได้ แพลตฟอร์มที่ให้บริการ PG Slot ควรมี ความปลอดภัยสูง
บทสรุปท้ายบท
สล็อต PG เป็นตัวเลือกยอดนิยมสำหรับผู้ที่ต้องการเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ ด้วยจุดเด่นด้าน ระบบลื่นไหล และการทำธุรกรรมที่ ทันใจ ผู้เล่นสามารถเริ่มต้นได้ ทันที ฝากถอนสะดวก และเลือกเกมได้ ครบทุกหมวด เหมาะสำหรับ ผู้เล่นทุกสไตล์ ในโลกของเกมสล็อตออนไลน์
tuan88
August 20, 2025tuan88
BradleyScali
August 20, 2025สล็อต PG เกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่คนค้นหาเยอะ เข้าเล่นไว ฝากถอนออโต้
คำค้นหา PG Slot มาแรงในช่วงนี้ ในกลุ่มผู้เล่นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ เพราะเป็น ผู้ให้บริการเกมสล็อตที่มาแรง ด้าน งานภาพคุณภาพสูง ความ นิ่งไม่สะดุด และ ระบบจ่ายที่ดึงดูด เกมของ PG พัฒนาโดยผู้ให้บริการชั้นนำ ที่รองรับการเล่นทั้งบน สมาร์ทโฟน และ พีซี
ความโดดเด่น ของ สล็อต PG
PG Slot เป็นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่ออกแบบมาให้ เข้าเกมไว เล่นผ่าน ระบบเว็บ และรองรับ ทุกแพลตฟอร์ม เข้าเล่นผ่านเว็บได้เลย ผู้เล่นสามารถเข้าเล่นผ่าน เว็บเบราว์เซอร์ ได้ทันที ภาพและเสียงถูกพัฒนาในรูปแบบ 3D ให้ความคมชัด พร้อมเอฟเฟกต์ จัดเต็ม
คุณสมบัติหลักของเกม pg slot ได้แก่
โบนัสและฟรีสปินหลายแบบ
ฟีเจอร์ตัวคูณรางวัล
เล่นฟรีก่อนเติมเงิน
รองรับภาษาไทยเต็มรูปแบบ
ฝากถอนง่าย ทำรายการไว
แพลตฟอร์ม PG Slot ส่วนใหญ่รองรับ การฝาก-ถอน ฝากถอนตลอดเวลา ขั้นต่ำเริ่มต้นเพียง หลักหน่วย ขึ้นอยู่กับ ระบบของผู้ให้บริการ การทำรายการใช้เวลา ไม่กี่วินาที ผ่าน QR Code หรือระบบ Mobile Banking ทำให้ธุรกรรมเป็นไปอย่าง ต่อเนื่อง
หมวดเกมฮิต ใน PG Slot
เกม สล็อต PG มีธีมหลากหลาย เช่น
ธีม เทพเจ้าและแฟนตาซี
ธีม ผจญภัย
ธีม เอเชียและโชคลาภ
ธีม Animal
ผู้เล่นนิยมเกมที่มีรอบพิเศษบ่อย พร้อมระบบ ฟีเจอร์พิเศษ และ โอกาสทำกำไรสูง เหมาะกับทั้ง คนเพิ่งเล่น และ สายสล็อตจริงจัง
ความน่าเชื่อถือ
สล็อต PG พัฒนาในระบบสากล มีการ ปกป้องข้อมูลผู้เล่น และใช้ระบบสุ่มผล Random Number Generator เพื่อให้ผลลัพธ์ โปร่งใส แพลตฟอร์มที่ให้บริการ สล็อต PG ควรมี ความปลอดภัยสูง
บทสรุปท้ายบท
PG Slot เป็นตัวเลือกยอดนิยมสำหรับผู้ที่ต้องการเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ ด้วยจุดเด่นด้าน โบนัสหลากหลาย และการทำธุรกรรมที่ รวดเร็ว ผู้เล่นสามารถเริ่มต้นได้ ไม่ซับซ้อน ฝากถอนสะดวก และเลือกเกมได้ จำนวนมาก เหมาะสำหรับ ทุกระดับประสบการณ์ ในโลกของเกมสล็อตออนไลน์