In Class 9 Physics, Inertia in physics is one of the first concepts students learn in the chapter Motion.
At first glance, it looks easy. But many students get confused when real-life examples are asked in exams.
You may have noticed:
You fall backwards when a bus starts suddenly
You fall forward when a bus stops suddenly
These effects happen because of inertia.
In this article, you’ll learn:
What inertia actually means
Types of inertia (clearly explained)
Bus and train examples
Why students often misunderstand inertia
Easy revision points for exams
What Is Inertia?

Inertia is the natural tendency of an object to resist any change in its state of motion or rest.
In simple words:
An object does not want to change what it is already doing.
This means:
If an object is at rest, it wants to stay at rest
If an object is moving, it wants to keep moving the same way
This property of matter is called inertia.
Inertia Depends on Mass
Heavier objects have more inertia than lighter ones.
Example:
It is easier to stop a bicycle than a truck
A loaded trolley is harder to push than an empty one
More mass = more inertia
Types of Inertia
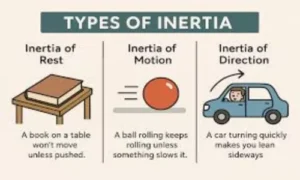
There are three types of inertia in physics.
Each type explains a different real-life situation.
1. Inertia of Rest
Definition:
The tendency of an object at rest to remain at rest unless acted upon by an external force.
Daily Life Examples:
A book lying on a table does not move on its own
Dust comes out of the carpet when it is beaten
Passengers fall backwards when a bus suddenly starts
2. Inertia of Motion
Definition:
The tendency of a moving object to continue moving with the same speed and direction.
Daily Life Examples:
A moving bicycle keeps rolling even after pedalling stops
You fall forward when a moving bus stops suddenly
Luggage on a bus slides forward when the brakes are applied
3. Inertia of Direction
Definition:
The tendency of an object to resist change in its direction of motion.
Daily Life Examples:
Mud flies off a rotating wheel tangentially
You lean sideways when a car takes a sharp turn
A stone tied to a string flies off in a straight line if the string breaks
Types of Inertia – Comparison Table
| Type of Inertia | Related To | Common Example |
|---|---|---|
| Inertia of Rest | Object at rest | Falling backwards in a starting bus |
| Inertia of Motion | Moving object | Falling forward in a stopped bus |
| Inertia of Direction | Change in direction | Leaning sideways in a turning car |
Bus and Train Examples
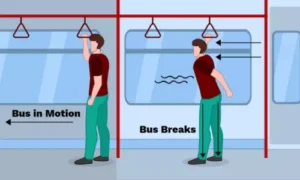
Why Do Passengers Fall Backwards When a Bus Starts Suddenly?
When the bus is at rest:
Your body is also at rest
When the bus suddenly moves:
Your feet move with the bus
Your upper body tends to remain at rest
This causes you to fall backwards.
This is due to the inertia of rest.
Why Do Passengers Fall Forward When a Bus Stops Suddenly?
When the bus is moving:
Your whole body is moving with it
When the bus stops suddenly:
Your feet stop with the bus
Your upper body keeps moving forward
This causes you to fall forward.
This is due to the inertia of motion.
Why Do Passengers Lean Sideways When a Car Turns?
When a car takes a sharp turn:
The car changes direction
Your body wants to continue in the original direction
This sideways effect happens due to the inertia of direction.
1. Confusing Force with Inertia
Students think inertia is a force.
This is wrong.
Inertia is a property of matter, not a force.
2. Mixing Up the Types
Students often:
Use the inertia of motion instead of rest
Forget the inertia of direction
Trick:
Start → inertia of rest
Stop → inertia of motion
Turn → inertia of direction
3. Not Visualising Real Life
Reading definitions without imagining real-life situations confuses.
Physics concepts become easy only when:
You connect them with daily experiences
4. Ignoring Mass Factor
Some students forget that inertia depends on mass.
That’s why:
Heavy objects resist motion more
Light objects change motion easily
Is Inertia Always Bad?
No. Inertia is useful too.
Positive Uses:
Seat belts work because of inertia
Flywheels store energy due to inertia
Vehicles maintain motion efficiently
Inertia helps maintain stability and smooth motion.
Quick Revision Points

Inertia is resistance to change
It depends on mass
Three types: rest, motion, direction
Bus start → inertia of rest
Bus stop → inertia of motion
Turning vehicle → inertia of direction
One-Line Definitions

Inertia: Property of matter to resist change in motion
Inertia of rest: Resistance to starting to move
Inertia of motion: Resistance to stopping moving
Inertia of direction: Resistance to changing direction
Conclusion
Inertia is not just a physics term—it is something you experience every day while travelling, walking, or even sitting in a vehicle.