Recently updated on December 21st, 2024 at 08:48 am
Reproduction is the foundation of life; consequently, it ensures species survival and the transmission of genetic material from one generation to the next. Furthermore, it involves a variety of biological systems, structures, and health considerations that all contribute to the formation of new life. In this regard, this blog investigates several aspects of reproduction, such as human reproductive systems, human reproduction, and the significance of reproductive health.
Human Reproductive Systems: Biological Framework
Reproductive systems are specialized structures and organs that produce, store, and transport gametes (sperm and eggs) and aid in fertilization.
Male Reproductive System
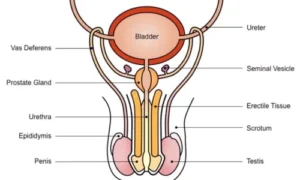
The male reproductive system is designed to create and transport sperm:
- Primary Organs: Specifically, the testes create sperm and testosterone.
- Supporting Structures: In addition, supporting structures include the epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and penis.
- Function: Notably, sperm generation (spermatogenesis) happens in the testes; thus, semen transports sperm during ejaculation.
The Female Reproductive System
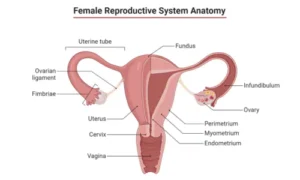
The female reproductive system promotes egg production and creates an environment for fertilization and fetal development.
- Primary Organs: The ovaries produce eggs (ova) and hormones such as estrogen and progesterone.
- In addition, Supporting Structures: Supporting structures include fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina.
- Furthermore, Functionality: During ovulation, the ovaries produce eggs, while the uterus nourishes and homes the developing fetus.
Human reproduction: the miracle of life
Human reproduction is a complex process that consists of multiple stages.
1. Gametogenesis
- Spermatogenesis: Spermatogenesis is the generation of sperm in the male testes.
- Oogenesis: Oogenesis is the formation of eggs in the female ovaries.
2. Fertilization
- The fallopian tube is where sperm and egg join to generate a zygote. This marks the beginning of a new life.
3. Implantation & Development
- The zygote separates to form a blastocyst, which attaches to the uterine wall. Over the next nine months, the embryo develops into a fetus.
4. Childbirth
- Childbirth At the end of pregnancy, the baby is born through the birth canal or by cesarean section.
Human Reproductive Health: The Key to Well-Being

Reproductive health refers to the physical, emotional, and social well-being associated with the reproductive system. It is critical to general health and quality of life.
Key Features of Reproductive Health
- Moreover, Education and Awareness: Understanding reproductive anatomy, safety precautions, and family planning is essential.
- Consequently, Preventive Care: Routine check-ups and screenings are necessary to detect and treat diseases such as infections, cancer, and hormone abnormalities.
- Additionally, Safe Practices: Use contraception to avoid unintended pregnancies and sexually transmitted illnesses.
- Furthermore, Nutrition and Lifestyle: A well-balanced diet and healthy lifestyle habits promote reproductive function.
- Lastly, Mental Health: Improving mental well-being, particularly during pregnancy, infertility, and menopause, is crucial.
Also See: Human Digestive System
Challenges in Human Reproductive Health
- STIs and Infections: (STIs) can influence fertility and overall health.
- Infertility: A global issue that frequently needs medical intervention.
- Access to Care: Many people do not have access to proper reproductive health treatments, which increases their risk.
- Cultural Stigmas: Misconceptions and taboos might inhibit open dialogue and appropriate care.
Conclusion
Reproduction is more than just a biological process; indeed, it is an essential part of life that requires awareness and care. Specifically, from the complexities of reproductive systems to the marvel of human reproduction and the importance of reproductive health, every part contributes to life’s survival and well-being. Therefore, we can secure a healthier future for individuals and communities by putting education, preventive measures, and healthcare access first.






