Have you ever wondered how your body fights off invaders and keeps you healthy? The secret lies in the seamless collaboration between two of your body’s most vital systems: the immune and lymphatic systems. 🦠💪Ever wondered how your body defends itself and stays healthy? The answer lies in the powerful teamwork between your immune and lymphatic systems. 🛡️🦠
While you may have heard of these systems individually, understanding how they work together is crucial for appreciating the incredible defence mechanisms your body employs daily. The immune system acts as your body’s army, while the lymphatic system serves as its highway and filtration network. Together, they form an unbeatable team that protects you from harmful pathogens and maintains your overall health.
In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into the fascinating world of immune-lymphatic synergy. You’ll discover how these systems collaborate to detect, trap, and eliminate threats, and learn about the intricate network of organs and tissues that make this possible. We’ll explore everything from the lymphatic system’s role in immune function to the immune system’s dependence on lymphatic pathways, and even uncover ways you can enhance this powerful partnership within your own body. 🧬🔬
1. Overview of the Immune and Lymphatic Systems
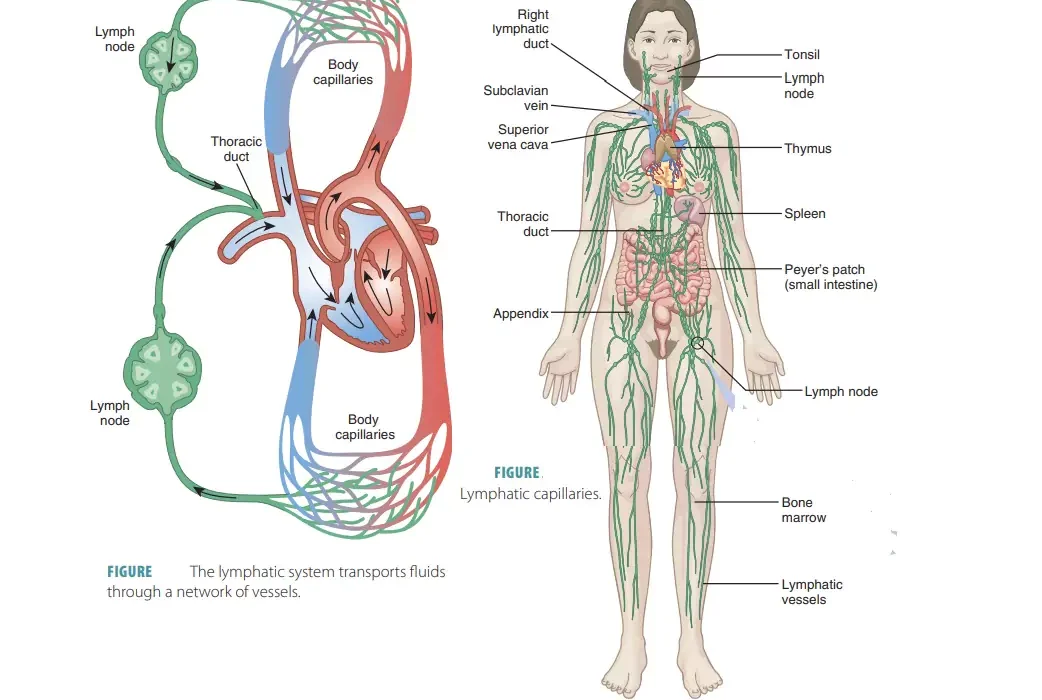
Key components of the immune system
Your immune system comprises various cells, tissues, and organs working together to defend your body. White blood cells, including T-cells and B-cells, play a crucial role in identifying and neutralising threats. Here’s a breakdown of key components:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| White Blood Cells | Identify and attack pathogens |
| Antibodies | Tag harmful substances for destruction |
| Lymph Nodes | Filter lymph and trap pathogens |
| Bone Marrow | Produces immune cells |
Essential elements of the lymphatic system
2. The Lymphatic System’s Role in Immune Function
Transportation of immune cells
The lymphatic system acts as a highway for immune cells, allowing them to travel efficiently throughout your body. This network of vessels transports lymphocytes, macrophages, and other immune cells to areas where they’re needed most. Here’s how the transportation process works:
- Immune cells enter the lymphatic vessels
- Lymph fluid carries cells through the lymphatic network
- Cells exit vessels at lymph nodes or infection sites
| Immune Cell Type | Primary Function | Transportation Method |
|---|---|---|
| Lymphocytes | Adaptive immunity | Lymphatic vessels |
| Macrophages | Innate immunity | Lymphatic and blood vessels |
Filtering and trapping pathogens
Your lymphatic system also serves as a crucial filter, trapping harmful pathogens before they can spread. Lymph nodes act as checkpoints, where immune cells encounter and neutralise threats. This filtering process is essential for maintaining your body’s defence against infections and diseases.
3. Immune System’s Dependence on Lymphatic Pathways
Lymph nodes as immune response centres
Lymph nodes serve as crucial hubs for your immune system’s defence operations. These small, bean-shaped structures are strategically located throughout your body, acting as filters and command centres. When pathogens enter your system, lymph nodes spring into action, trapping harmful invaders and initiating immune responses.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Filtration | Traps pathogens and foreign particles |
| Activation | Stimulates T and B lymphocytes |
| Coordination | Facilitates communication between immune cells |
Lymphatic vessels facilitate immune cell movement
Your lymphatic vessels form an intricate network that enables immune cells to travel efficiently throughout your body. This system of tubes works in tandem with your blood circulation, ensuring that immune cells can reach infection sites quickly and effectively.
3. Collaborative Defence Mechanisms
Antigen presentation in lymph nodes
Lymph nodes play a crucial role in your immune defence. As antigens enter your body, they’re transported to lymph nodes where specialised cells present them to T cells. This process triggers your adaptive immune response, preparing your body to fight specific pathogens.
Activation of adaptive immune responses
| Adaptive Immune Response | Function |
|---|---|
| T cells | Recognise specific antigens |
| B cells | Produce antibodies |
| Memory cells | Provide long-term immunity |
Your adaptive immunity is activated when T and B cells in lymph nodes recognise antigens. This leads to:
- Clonal expansion of specific lymphocytes
- Production of antibodies
- Formation of memory cells for future protection
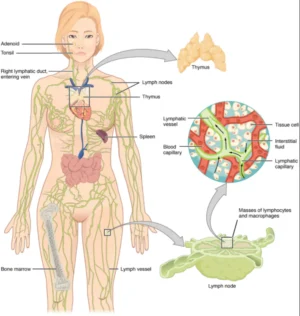
4. Interconnected Organs and Tissues
Interconnected Organs and Tissues
Thymus gland and T-cell development
Your thymus gland plays a crucial role in your immune system’s development. It’s where T-cells mature, becoming specialised defenders against infections. As you age, your thymus shrinks, but its early work remains vital for your lifelong immunity.
Bone marrow and immune cell production
Your bone marrow is the birthplace of various immune cells. It produces B-cells, which create antibodies, and stem cells that develop into other immune cell types. This continuous production ensures your body always has fresh defenders ready to combat invaders.
| Organ | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Thymus | T-cell maturation |
| Bone Marrow | Immune cell production |
5. Enhancing Immune-Lymphatic Synergy
Lifestyle factors supporting both systems
Your lifestyle choices significantly impact your immune and lymphatic systems. Regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management are crucial for optimal function. Here’s a quick guide:
| Lifestyle Factor | Impact on Immune-Lymphatic Synergy |
|---|---|
| Exercise | Boosts lymph flow and immune cells |
| Sleep | Enhances immune response |
| Stress Management | Reduces inflammation |
Nutritional support for optimal function
Proper nutrition is vital for maintaining a strong immune-lymphatic connection. Focus on a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. Include:
- Citrus fruits (Vitamin C)
- Leafy greens (Vitamin A)
- Nuts and seeds (Zinc and Omega-3)
Conclusion
The immune and lymphatic systems form a powerful alliance in your body’s defence network. By working together, they create a comprehensive shield against pathogens and maintain your overall health. The lymphatic system serves as a crucial highway for immune cells, while the immune system relies on lymphatic pathways to effectively combat invaders throughout your body.
Understanding this synergy can help you appreciate the importance of maintaining both systems. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and proper hydration, you can enhance the collaboration between your immune and lymphatic systems. Remember, a strong immune-lymphatic partnership is key to your body’s ability to fight off infections and maintain optimal health.