Recently updated on September 2nd, 2025 at 07:41 am
Edwin Hubble’s (1889–1953) groundbreaking discoveries dramatically reshaped our understanding of the universe. Born on November 20, 1889, in Marshfield, Missouri, Hubble showed early talent in both academics and athletics. He later pursued higher education at the University of Chicago, where he earned a degree in mathematics and astronomy in 1910, laying the foundation for his future contributions to modern cosmology.
He attended Oxford University as a Rhodes Scholar, where he got a law degree in 1913; however, his interest in science would ultimately lead to his career.

Early Career and World War One
After finishing his studies, Hubble taught high school physics and basketball; nevertheless, he quickly returned to astronomy. In 1917, he received his doctorate from the University of Chicago, where he studied at the Yerkes Observatory.
Moreover, his dissertation focused on nebulae, which were previously assumed to be gas clouds in the Milky Way. Unfortunately, his career was momentarily halted by World War I when he served in the United States Army.
Contributions in Astronomy
In 1919, Hubble joined the Mount Wilson Observatory in California, which housed the enormous Hooker Telescope, the world’s largest at the time. **Consequently**, it was there that he made his most significant findings
1. The Existence of Other Galaxies: In the early 1920s, Hubble discovered Cepheid variable stars in the Andromeda Nebula and, consequently, utilised their periodic brightness to calculate their distance.
As a result, he established that Andromeda was far beyond the Milky Way, indicating that the cosmos contained additional galaxies—a discovery that, undoubtedly, profoundly altered cosmology.
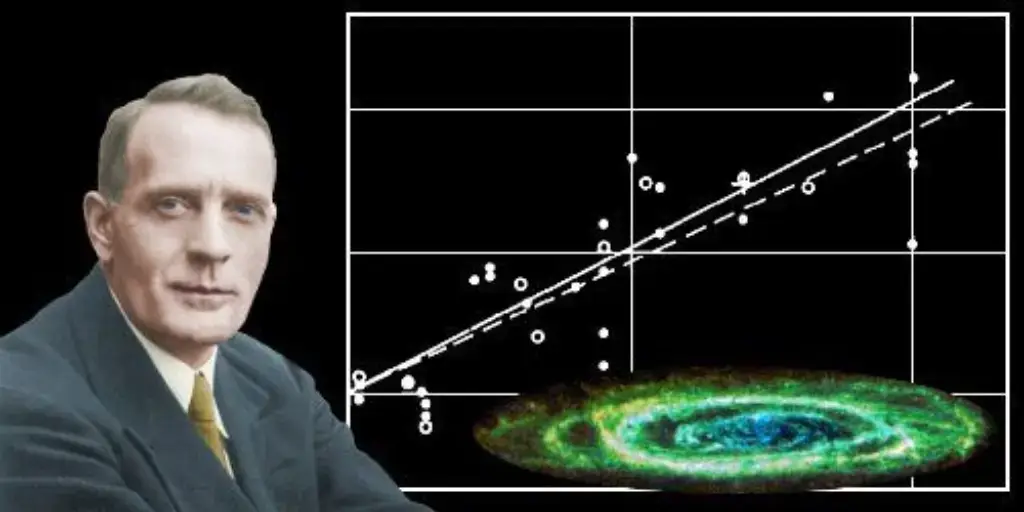
2. Hubble’s Law: In 1929, Hubble demonstrated that galaxies move away from one another; furthermore, their speed is proportional to their distance. This significant discovery, therefore, gave the first observational evidence for an expanding cosmos, ultimately laying the groundwork for the Big Bang theory.
The proportional relationship he discovered is now known as Hubble’s Law, and the constant of proportionality is the Hubble Constant.
Edwin Hubble’s Recognition and Legacy
Hubble’s accomplishments garnered him countless honours during his life. Nevertheless, he was upset that he never got the Nobel Prize because astronomy was not considered a branch of physics at the time.

The Hubble Space Telescope, which launched in 1990, is named after him. Moreover, this telescope has continued to advance our understanding of the cosmos, taking stunning photos and revealing information about cosmic phenomena such as black holes, dark matter, and the universe’s age.
Edwin Hubble died on September 28, 1953, in San Marino, California; however, his impact continues. His study not only demonstrated the enormity of the universe but also signalled the start of contemporary observational astronomy.
Edwin Hubble’s discoveries:
Edwin Hubble’s discoveries transformed astronomy and cosmology, influencing our present knowledge of the world. His main contributions include:
1. Discovery of Other Galaxies
- What He Discovered: In 1924, Hubble revealed that the “Andromeda Nebula” (now known as the Andromeda Galaxy) was not a gas cloud within the Milky Way, but rather a galaxy far beyond it.
- How He Did It: Hubble used Mount Wilson Observatory’s Hooker Telescope to identify Cepheid variable stars in Andromeda. By estimating their distances using the period-luminosity connection, he demonstrated that Andromeda was far beyond the Milky Way’s bounds.
- Significance: This was the first clear evidence that the universe includes galaxies other than the Milky Way, which broadened our understanding of its vastness.
2. Hubble’s Law and the Expanding Universe
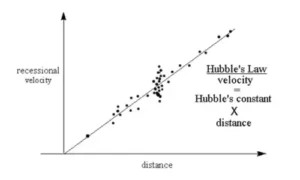
- What He Found: In 1929, Hubble discovered that galaxies are receding from us and that their recessional velocity is related to their distance from Earth. This relationship became known as Hubble’s law.
- Key Formula: 𝑣 = 𝐻 0 × 𝑑 v=H 0×d
Here, 𝑣 is the velocity, 𝑻 is the Hubble constant, and 𝑑 is the distance. - Significance: Hubble’s finding gave the first observational evidence for the expanding cosmos, confirming Georges Lemaître’s theoretical predictions and paving the way for the Big Bang theory.
3. Classification of Galaxies
- What He Discovered: Hubble developed the Hubble Sequence, sometimes known as “Hubble’s Tuning Fork,” a mechanism for classifying galaxies based on their form and structure. Specifically, there are several types of galaxies:
- Firstly, Elliptical galaxies (E)
- Secondly, Spiral Galaxies (S)
- Additionally, Barred Spiral Galaxies (SB)
- Finally, Irregular galaxies
Significance: This system continues to be a key component of galaxy morphology research, assisting astronomers in understanding galactic evolution and structure.
4. The universe is larger than expected
- What He Discovered: By measuring distances between galaxies, Hubble demonstrated that the observable universe is much larger than previously imagined.
- Significance: This broke the previous belief that the Milky Way was the entirety of the cosmos, drastically altering humanity’s cosmic perspective.
5. Foundation of Modern Cosmology
- What He Found: Hubble’s observations laid the groundwork for many important cosmological hypotheses, including the Big Bang theory and research into dark matter and dark energy.
- Significance: His work contributed to the establishment of observational cosmology as a prominent scientific subject.
Hubble’s discoveries are among the most significant in the history of science, showing the universe’s scale, structure, and dynamic character. They significantly transformed our concept of the universe and humankind’s place in it.
Edwin Bubble is famous
1. Discovery of Galaxies beyond the Milky Way
Hubble demonstrated that the “nebulae” visible in the night sky, such as the Andromeda Nebula, were whole galaxies far beyond the Milky Way. This discovery demonstrated that the cosmos is much larger than previously thought.
2. Hubble’s Law and the Expanding Universe
Hubble established the link between galaxies’ distances and velocities, demonstrating that galaxies are migrating apart. This observation led to Hubble’s Law, which shows that the universe is expanding. This discovery provided the basis for the Big Bang theory.
3. Classification of Galaxies
- Hubble created the Hubble Sequence, sometimes known as “Hubble’s Tuning Fork,” which divides galaxies into ellipticals, spirals, and irregulars based on their morphological characteristics.
Legacy
- Hubble’s work changed our knowledge of the universe and laid the groundwork for contemporary observational cosmology.
- The Hubble Space Telescope, dedicated in his honour, continues to explore and uncover the wonders of the universe, adding to his legacy.
- Hubble’s discoveries transformed astronomy, broadening our understanding of the cosmos and our role in it.
conclusion:
Finally, Edwin Hubble’s work transformed our view of the universe, cementing his reputation as one of history’s most prominent astronomers. Hubble radically changed humanity’s understanding of the cosmos by discovering galaxies beyond the Milky Way and realising that the universe is expanding.
His contributions established the foundation for contemporary cosmology, including the Big Bang idea, and created tools and frameworks, such as the Hubble Sequence, that continue to govern astronomical research.
His legacy lives on not only via his findings but also through the Hubble Space Telescope, which bears his name and gazes into the stars, unearthing new mysteries about the cosmos.






filmproductioncortina-874
November 29, 2024ORBS Production https://filmproductioncortina.com is a full-service film, photo and video production company in Cortina d’Ampezzo and the Dolomites. We create commercials, branded content, sports and winter campaigns with local crew, alpine logistics, aerial/FPV filming and end-to-end production support across the Alps. Learn more at filmproductioncortina.com
1win-989
November 29, 20241win зеркало промокод 1win
federatsia-516
November 29, 2024Хочешь развлечься? купить альфа пвп федерация – это проводник в мир покупки запрещенных товаров, можно купить гашиш, купить мефедрон, купить кокаин, купить меф, купить экстази, купить альфа пвп, купить гаш в различных городах. Москва, Санкт-Петербург, Краснодар, Владивосток, Красноярск, Норильск, Екатеринбург, Мск, СПБ, Хабаровск, Новосибирск, Казань и еще 100+ городов.
bonus-casino-452
November 29, 2024бонуси в казино казино з бонусами
slots-online-738
November 29, 2024слоти безкоштовно найкращі слоти
casino-games-628
November 29, 2024ігри казино онлайн ігри казино онлайн
mostbet-9
November 29, 2024oficjalne pobieranie mostbet mostbet osobisty
belarus-news-189
November 29, 2024самые последние новости беларусь новости беларуси
novosti-belarus-423
November 29, 2024самые свежие новости беларуси зеркало новости беларусь
kraken
November 29, 2024Надежный кракен официальный сайт доступен через онион адреса и клир-зеркала с автоматическим перенаправлением на защищенное соединение в Tor сети.
medim-pro-76
November 29, 2024Лучшее собрано здесь: https://medim-pro.ru/kupit-psikhiatricheskoe-osvidetelstvovanie/
emerald-chat-214
November 29, 2024Free video chat emerald chat features find people from all over the world in seconds. Anonymous, no registration or SMS required. A convenient alternative to Omegle: minimal settings, maximum live communication right in your browser, at home or on the go, without unnecessary ads.
EdwinSib
November 29, 2024Read More: https://hyperwarped.com/kupit-akkaunty-fejsbuk-fb-dlja-reklamy-i-targeta-10/
kraken 678
November 29, 2024Проверенная рабочая кракен ссылка из всплывающего окна после авторизации гарантирует подлинность адреса и безопасное соединение с оригинальной площадкой.
nv-casino-770
November 29, 2024Uwielbiasz hazard? https://online-nv-casino.com: rzetelne oceny kasyn, weryfikacja licencji oraz wybor bonusow i promocji dla nowych i powracajacych graczy. Szczegolowe recenzje, porownanie warunkow i rekomendacje dotyczace odpowiedzialnej gry.
dispatch42-612
November 29, 2024Нужна работа в США? школа трак диспетчинга в сша для смены профессии : работа с заявками и рейсами, переговоры на английском, тайм-менеджмент и сервис. Подходит новичкам и тем, кто хочет выйти на рынок труда США и зарабатывать в долларах.
LanceObeks
November 29, 2024Go for details: https://markets.financialcontent.com/sandiego/article/abnewswire-2025-12-4-the-ultimate-guide-to-buying-facebook-advertising-accounts-what-must-be-known/
kraken-730
November 29, 2024Криптографическая верификация показывает как проверить кракен ссылку через импорт официального PGP ключа в GPG и выполнение команды verify для подписанного сообщения с адресом.
kraken-562
November 29, 2024Актуальная кракен ссылка обновляется администрацией площадки ежемесячно для обхода блокировок провайдеров и обеспечения стабильного доступа к маркетплейсу.
DonaldOdort
November 29, 2024Современный шоп по ссылке предлагает доступ приобрести прогретые расходники для работы. Ключевое преимущество этого шопа — заключается в наличии масштабной базы знаний, в которой выложены секретные мануалы по заливу. Здесь можно найти страницы FB, Insta, TG, Discord под любые цели: начиная с пустышек до агентскими кабинетами с друзьями. Заказывая здесь, клиент получает не только куки, но и всестороннюю помощь саппорта, гарантию на момент покупки и самые приятные прайсы в нише.
1xbet-burkina-631
November 29, 2024La plateforme 1xbet apk burkina: paris sportifs en ligne, matchs de football, evenements en direct et statistiques. Description du service, marches disponibles, cotes et principales fonctionnalites du site.
1xbet-congo-151
November 29, 2024Site web 1xbet cd apk – paris sportifs en ligne sur le football et autres sports. Propose des paris en direct et a l’avance, des cotes, des resultats et des tournois. Description detaillee du service, des fonctionnalites du compte et de son utilisation au Congo.
parifoot-188
November 29, 2024Site web de pari foot rdc: paris sportifs, championnats de football, resultats des matchs et cotes. Informations detaillees sur la plateforme, les conditions d’utilisation, les fonctionnalites et les evenements sportifs disponibles.
1xbet-burkina-faso-467
November 29, 2024La plateforme en ligne 1xbet burkina faso: paris sportifs en ligne, matchs de football, evenements en direct et statistiques. Description du service, marches disponibles, cotes et principales fonctionnalites du site.
1xbet-apk-239
November 29, 2024Application mobile 1xbet apk burkina. Paris sportifs en ligne, football et tournois populaires, evenements en direct et statistiques. Presentation de l’application et de ses principales fonctionnalites.
stomatologiya-voronezh-349
November 29, 2024Современная Стоматология в Воронеже лечение кариеса, протезирование, имплантация, профессиональная гигиена и эстетика улыбки. Квалифицированные специалисты, точная диагностика и забота о пациентах.
Binance账户
November 29, 2024Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Caryl Winterfeldt
November 29, 2024I am not sure where you’re getting your information, but great topic. I needs to spend some time learning more or understanding more. Thanks for wonderful info I was looking for this info for my mission.
slottica kasyno
November 29, 2024Dlaczego warto wybrać Slottica? Nasza oferta regularnie się powiększa dzięki współpracy z najlepszymi dostawcami, takimi jak Novomatic, BGaming, Play’n Go, Gamzix, NetEnt czy Playson. Dzięki temu każdy znajdzie coś odpowiedniego dla siebie – od klasyki po nowoczesne gry z zaawansowaną grafiką. Kasyno obsługuje wygodne metody płatności, w tym Blik (zgodny z bankami, takimi jak mBank, ING, PKO BP, Pekao czy Millennium), a także karty Visa i Mastercard. Liczne pozytywne opinie na platformach takich jak Trustpilot czy Opinie pokazują, że Slottica to miejsce godne zaufania. Dla fanów mobilnej rozrywki przygotowaliśmy aplikację na systemy iOS oraz Android, zapewniającą płynną rozgrywkę na nowoczesnych urządzeniach.
https://winterfriend.com/
November 29, 2024References:
Cannery casino las vegas
References:
https://winterfriend.com/
https://jackiecycle.com/43/?bmode=view&idx=66409487
November 29, 2024References:
Punto banco
References:
https://www.snoopygarden.com/sn_event/?bmode=view&idx=132356354
www.realitateavalceana.ro
November 29, 2024References:
Blackjack
References:
https://ufabet888vip.xyz/slot999-%e0%b8%aa%e0%b8%a5%e0%b9%87%e0%b8%ad%e0%b8%95%e0%b9%80%e0%b8%a7%e0%b9%87%e0%b8%9a%e0%b8%95%e0%b8%a3%e0%b8%87-%e0%b8%a3%e0%b8%b0%e0%b8%9a%e0%b8%9a%e0%b8%ad%e0%b8%ad%e0%b9%82%e0%b8%95%e0%b9%89/
us.kdocinc.com
November 29, 2024References:
Blackjack knives
References:
https://youth.happy-you.kr/53/?bmode=view&idx=167139762