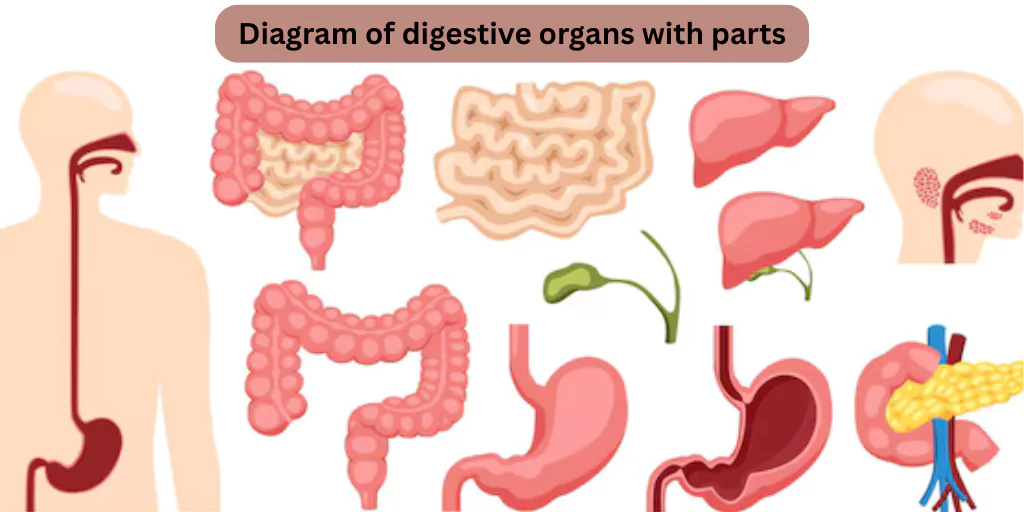
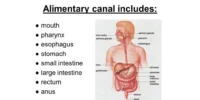
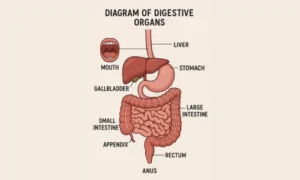
Draw a diagram of digestive organs with correct labels to understand how the human body obtains the energy and nutrients it needs to function properly. Before the body can use food, it must be broken down into simpler forms—a task performed by the digestive system. This complex system is made up of various organs that work together to break down food, absorb nutrients, and remove waste.
Digestive Organs with Parts and Functions (Explained)
1. Mouth
Parts: Teeth, tongue, salivary glands
Function:
- Teeth break down food mechanically.
- Saliva softens food and starts digestion with enzymes like amylase.
- The tongue helps in mixing and swallowing.
2. Pharynx and Esophagus
Pharynx: Connects the mouth to the esophagus
Esophagus: Muscular tube
Function:
- Transports food to the stomach via peristalsis (muscular movements).
3. Stomach
Parts: Cardiac sphincter, fundus, body, pyloric sphincter
Function:
- Stores food and mixes it with gastric juices.
- Breaks down proteins with pepsin and HCl.
- Converts food into a semi-liquid called chyme.
4. Small Intestine
Parts: Duodenum, jejunum, ileum
Function:
- The duodenum receives bile and pancreatic juices.
- The main site of digestion and nutrient absorption.
5. Large Intestine
Parts: Cecum, colon (ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid), rectum
Function:
- Absorbs water and minerals.
- Forms and stores faeces.
6. Anus
Function:
- Removes solid waste from the body.
Accessory Digestive Organs
These help digestion but are not part of the alimentary canal
Liver
- Produces bile (helps digest fats)
Gallbladder
- Stores and releases bile into the small intestine
Pancreas
- Produces digestive enzymes and insulin
Labelled Diagram Overview
Here’s what a labelled digestive system diagram typically includes:
- Mouth
- Pharynx
- Esophagus
- Stomach
- Liver
- Gallbladder
- Pancreas
- Small Intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum)
- Large Intestine (colon sections)
- Rectum
- Anus
Conclusion
The digestive system is a key element of the human body that breaks down food, absorbs nutrients, and eliminates waste. Each organ, from the mouth to the anus, has a specific purpose in this intricate but well-organised process. Supporting organs such as the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder produce enzymes and fluids to facilitate digestion. These organs work together to ensure that the body has enough fuel and nutrients to develop, heal, and function effectively.