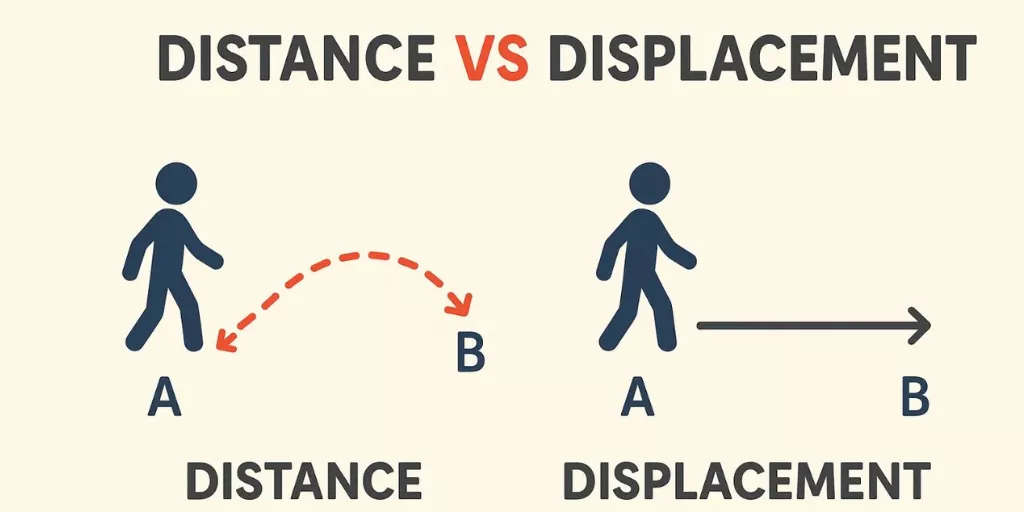
In Class 9 Physics, Distance and Displacement is one of the most important topics from Motion.
Many students lose marks because they think both are the same, but they are not.
This chapter is frequently asked in:
Board exams
Unit tests
MCQs
Numerical problems
In this article, you will learn:
What distance is
What displacement is
Key differences (table)
A simple diagram
3 solved numericals
What Is Distance?

Distance is the total length of the path travelled by an object.
Key Points:
It tells how much ground is covered
It does not care about direction
It is always positive
It depends on the actual path taken
Example:
If you walk from home to a shop and come back, the distance is the full path travelled, even though you returned to the same place.
What Is Displacement?
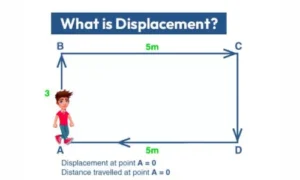
Displacement is the shortest straight-line distance between the starting point and the ending point, along with direction.
Key Points:
It tells how far and in which direction
Direction matters
It can be zero
It depends only on the initial and final positions
Example:
If you go from home to a shop and return home, your displacement is zero because the start and end points are the same.
Distance vs Displacement
| Basis | Distance | Displacement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total path covered | Shortest straight-line distance |
| Direction | Not required | Required |
| Type of quantity | Scalar | Vector |
| Can it be zero? | No (if motion occurred) | Yes |
| Path dependent | Yes | No |
| Value | Always positive | Can be positive, negative, or zero |
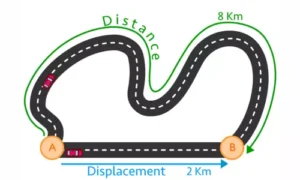
Simple Diagram: Distance vs Displacement

Diagram Explanation:
Curved path → Distance
Straight line between start and end → Displacement
Important Differences Explained Simply
1. Path Matters
Distance changes if the path changes
Displacement remains the same if the start and end points are the same
2. Direction Importance
Distance ignores direction
Displacement always includes direction
3. Zero Case
Distance cannot be zero if movement happens
Displacement can be zero even after movement
Solved Numericals (Class 9 Level)
Numerical 1
A boy walks 5 m east and then 3 m west.
Find:
Distance travelled
Displacement
Solution
Distance
Total path = 5 m + 3 m = 8 m
Displacement
Net movement = 5 − 3 = 2 m east
Answer:
Distance = 8 m
Displacement = 2 m east
Numerical 2
A student runs 10 m north, then 10 m south, and stops.
Find:
Distance
Displacement
Solution
Distance
10 m + 10 m = 20 m
Displacement
Starting point = Ending point
So displacement = 0 m
Answer:
Distance = 20 m
Displacement = 0 m
Numerical 3
A car moves 6 km east and then 8 km north.
Find:
Distance
Displacement
Solution
Distance
6 km + 8 km = 14 km
Displacement
Shortest straight-line distance ≈ 10 km (diagonal)
Answer:
Distance = 14 km
Displacement ≈ 10 km
Common Mistakes Students Make

Writing distance when direction is given
Saying displacement is always greater than distance
Forgetting displacement can be zero
Not mentioning direction in displacement answers
Quick Revision Points

Distance = total path
Displacement = shortest path with direction
Distance ≥ Displacement
Displacement can be zero
Distance is scalar, displacement is vector
Why This Topic Is Important for Class 9
Forms the base for Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration
Direct questions in exams
Used in higher classes (Physics core concept)
Conclusion
Distance and displacement may look similar, but they describe different aspects of motion.
Understanding their difference helps you: