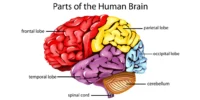
The human brain is one of the body’s most complicated organs, regulating everything from movement and memory to emotions and decision-making. Disorders or diseases that impair brain function can have a profound and far-reaching impact on one’s life. Understanding these diseases, their origins, and treatment options is crucial for maintaining brain health.
What are Brain Disorders and Diseases?
Brain illnesses and diseases are ailments that disrupt the brain’s normal function. They may be structural (damage to brain tissue), functional (chemical imbalances), or a combination of the two.
Common Types of Brain Disorders
1. Neurodegenerative Diseases
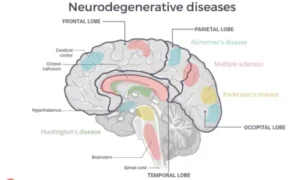
These are progressive conditions that damage brain cells over time.
- Examples: Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease
- Symptoms: Memory loss, tremors, difficulty in movement, confusion
2. Cerebrovascular Disorders
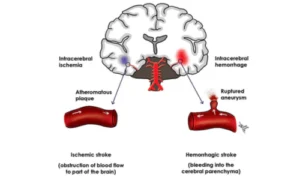
Disorders that affect blood flow to the brain.
- Examples: Stroke, aneurysm, transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- Symptoms: Sudden weakness, paralysis, speech difficulties, vision problems
3. Infectious Brain Diseases
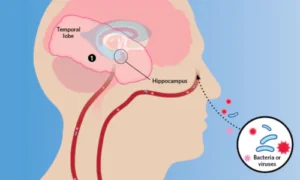
Caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites.
- Examples: Meningitis, encephalitis, brain abscess
- Symptoms: Fever, headache, neck stiffness, seizures
4. Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBI)

Caused by accidents, falls, or head injuries.
- Examples: Concussion, skull fractures, brain haemorrhage
- Symptoms: Dizziness, unconsciousness, confusion, memory problems
5. Mental and Psychiatric Disorders

Brain chemistry imbalances that affect emotions and behaviour.
- Examples: Depression, anxiety disorders, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder
- Symptoms: Mood swings, hallucinations, persistent sadness, fear
Causes of Brain Disorders
- Genetic mutations and hereditary conditions
- Infections and autoimmune diseases
- Injury or trauma
- Poor blood circulation
- Lifestyle factors like stress, poor diet, or substance abuse
Diagnosis of Brain Diseases
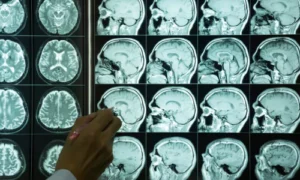
Doctors use advanced techniques to detect brain disorders:
- MRI and CT scans
- EEG (Electroencephalogram)
- Blood tests and neurological exams
- Cognitive and memory assessments
Treatment Options
- Medications: For managing symptoms (antidepressants, anti-seizure drugs)
- Therapies: Physical, occupational, and speech therapy
- Surgery: For tumours, aneurysms, or severe trauma
- Lifestyle Changes: Healthy diet, stress management, brain exercises
Prevention and Brain Health Tips
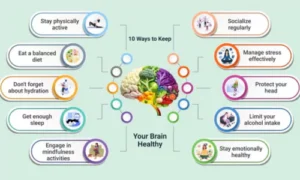
1. Eat a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids
2. Exercise regularly for better blood circulation
3. Protect your head from injuries
4. Avoid smoking, drugs, and excessive alcohol
5. Engage in brain activities like puzzles and reading
Conclusion
Brain problems and diseases can range from minor to life-threatening. Early detection, effective medical care, and a healthy lifestyle are all important in safeguarding the brain. Awareness is the first step towards prevention and better treatment outcomes.
FAQs
1. What are the most common brain diseases?
Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, Parkinson’s disease, and depression are among the most common.
2. Can brain disorders be cured?
Some brain disorders can be treated or managed effectively, but many require lifelong care.
3. How do I know if I have a brain problem?
Persistent headaches, memory loss, confusion, seizures, or sudden mood changes may indicate brain issues.
4. Which lifestyle changes protect the brain?
Regular exercise, a healthy diet, mental stimulation, and stress control help protect brain health.
5. Can mental disorders be considered brain diseases?
Yes, many mental disorders are linked to brain chemistry and function, so they fall under brain-related diseases.