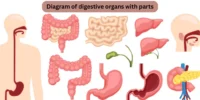
The Alimentary Canal of Human is a remarkable structure that forms the foundation of the digestive process. Extending from the mouth to the anus, it systematically breaks down the food we eat, ensuring the absorption of nutrients and the removal of waste from the body.
What is the Alimentary Canal?
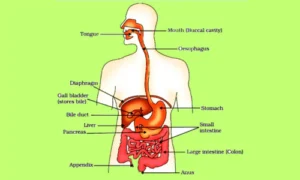
The alimentary canal, commonly referred to as the digestive system, is a continuous, hollow tube in the human body that begins in the mouth and terminates in the anus. It is approximately 9 meters (30 feet) long in an adult and is responsible for food intake, digestion, absorption, and excretion.
Main Components of the Human Alimentary Canal
Let’s look at the primary components of the alimentary canal and their distinct functions:
1. Mouth
Structure: Includes lips, tongue, teeth, and salivary glands.
Function: The entry point for food; mechanical breakdown by chewing and chemical digestion by saliva.
2. Pharynx
Structure: A muscular funnel connecting the mouth to the esophagus.
Function: Pathway for the movement of food from the mouth to the esophagus.
3. Esophagus
Structure: A long, muscular tube (~25 cm).
Function: Transports food to the stomach using wave-like muscle contractions called peristalsis.
4. Stomach
Structure: A J-shaped muscular sac.
Function: Mixes food with gastric juices for chemical digestion; converts it into a semi-liquid form called chyme.
5. Small Intestine
Structure: Divided into three parts – duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
Function: Major site for the digestion and absorption of nutrients into the bloodstream.
6. Large Intestine
Structure: Includes cecum, colon, rectum, and anus.
Function: Absorbs water and minerals; forms and stores faeces.
7. Anus
Structure: The terminal opening of the alimentary canal.
Function: Removes undigested and unwanted waste from the body.
Supporting Digestive Organs (Not Part of the Canal)
While not directly part of the canal, these accessory organs play a vital role in digestion:
- Salivary glands: Secrete saliva to help break down food.
- Liver: Produces bile to digest fats.
- Gallbladder: Stores and releases bile.
- Pancreas: Releases enzymes that aid in digestion in the small intestine.
Functions of the Alimentary Canal
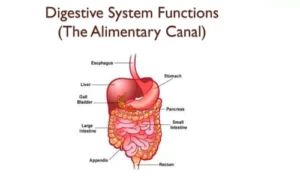
The alimentary canal performs several key functions:
- Ingestion – Taking food into the mouth.
- Digestion – Breaking down food both mechanically and chemically.
- Absorption – Transporting nutrients into the blood for energy and growth.
- Assimilation – Using absorbed nutrients in body cells.
- Egestion – Removing indigestible substances as waste (faeces).
Interesting Facts
- The small intestine is longer than the large intestine but narrower.
- The stomach’s acid is strong enough to dissolve metal, but your stomach is protected by a mucus lining.
- Peristalsis in the esophagus is so strong that you could swallow even upside down!
Conclusion
The human alimentary canal is a fascinating and necessary component of our bodies that keeps us active, healthy, and functional. Understanding its structure and function not only broadens our biological knowledge but also enables us to make better lifestyle and food decisions.





production company
July 17, 2025need a video? video production agency in italy offering full-cycle services: concept, scripting, filming, editing and post-production. Commercials, corporate videos, social media content and branded storytelling. Professional crew, modern equipment and a creative approach tailored to your goals.
faamru
July 17, 2025Продажа тяговых https://faamru.com аккумуляторных батарей для вилочных погрузчиков, ричтраков, электротележек и штабелеров. Решения для интенсивной складской работы: стабильная мощность, долгий ресурс, надёжная работа в сменном режиме, помощь с подбором АКБ по параметрам техники и оперативная поставка под задачу
ab-resurs
July 17, 2025Продажа тяговых https://ab-resurs.ru аккумуляторных батарей для вилочных погрузчиков и штабелеров. Надёжные решения для стабильной работы складской техники: большой выбор АКБ, профессиональный подбор по параметрам, консультации специалистов, гарантия и оперативная поставка для складов и производств по всей России
kraken
July 17, 2025Актуальная ссылка площадки на рабочая ссылка кракен с защитой от фишинга и мошеннических копий сайта
RobertDow
July 17, 2025Продажа тяговых ab-resurs.ru аккумуляторных батарей для вилочных погрузчиков и штабелеров. Надёжные решения для стабильной работы складской техники: большой выбор АКБ, профессиональный подбор по параметрам, консультации специалистов, гарантия и оперативная поставка для складов и производств по всей России
Stanleywiz
July 17, 2025Продажа тяговых faamru.com аккумуляторных батарей для вилочных погрузчиков, ричтраков, электротележек и штабелеров. Решения для интенсивной складской работы: стабильная мощность, долгий ресурс, надёжная работа в сменном режиме, помощь с подбором АКБ по параметрам техники и оперативная поставка под задачу
Georgegus
July 17, 2025Лучший дилер https://accounts-marketplace2000.com предоставляет возможность купить рекламные сущности для работы. Когда вы планируете купить аккаунт Facebook для рекламы, обычно задача не в «просто доступе», а в контроле и порядке: предсказуемая операционка, понятные роли между участниками и ясные доступы. Мы подготовили короткую карту выбора, чтобы вы сразу понимали что сравнивать перед покупкой.Коротко: с чего начать: откройте базовых разделов TikTok, а если нужен перформанс — идите напрямую в разделы под рекламу: Google Ads. Важно: покупка — это только вход. Дальше решает порядок: как выдаются права, как вы ведете кампании аккуратно, как документируете действия и как разделяете тестовые и стабильные процессы. Гордость данной площадки — заключается в наличии масштабной образовательной секции, в которой опубликованы рабочие инструкции по операционке. Мы подскажем, каким образом грамотно выстроить процесс, чтобы вы старт был предсказуемым а также соблюдались правила . Заказывая здесь, клиент получает не просто состав, но и полную консультацию, ясное описание, гарантию на момент покупки и максимально адекватные цены на рынке. Дисклеймер: действуйте в рамках закона и всегда с учетом правил сервисов.
Trading Forex
July 17, 2025Outstanding post however I was wanting to know
if you could write a litte more on this topic? I’d be very thankful if you could elaborate a little bit further.
Appreciate it!
Trading Emas
July 17, 2025What’s up, yeah this piece of writing is genuinely fastidious and I have learned lot of things from it regarding blogging.
thanks.
Belajar Trading
July 17, 2025Attractive component to content. I just stumbled
upon your site and in accession capital to say
that I get actually loved account your weblog posts.
Anyway I’ll be subscribing on your augment and even I success you access constantly fast.