If you are learning physics for students, you may have heard words like speed, velocity, and acceleration.
Many students think acceleration means “going fast”, but that is not fully correct.
In this article, we will explain what acceleration really means, using simple words, daily life examples, and easy numericals that are commonly asked in school exams.
Definition of Acceleration
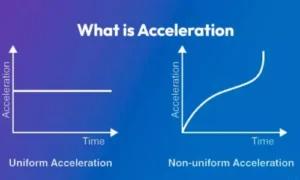
Acceleration is the rate at which the velocity of an object changes with time.
That’s it—one simple line.
This change can be:
- Increase in speed
- Decrease in speed
- Change in direction
Understanding Acceleration in Simple Words
Acceleration does not only mean “speeding up”.
An object is accelerating if:
- It becomes faster
- It becomes slower
- It changes its direction
Even if speed stays the same but direction changes, acceleration is present.
Daily Life Examples of Acceleration

Let us understand acceleration through real-life situations you see every day.
1. Bus Starting from a Stop
When a bus starts moving from a bus stop, its speed increases from zero to some value.
This increase in speed means the bus is accelerating.
2. Car Applying Brakes
When a moving car applies the brakes, its speed decreases.
This is also acceleration, but in the opposite direction (called deceleration).
3. Fan Switching On
When you switch on a fan, it slowly increases speed before reaching full speed.
That gradual increase is acceleration.
4. Turning a Bicycle
If you ride a bicycle at the same speed but take a turn, the direction changes.
Even though speed is constant, velocity changes — so acceleration exists.
5. Lift Moving Up or Down
When a lift starts or stops, its speed changes.
That change causes acceleration.
Relation Between Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration

Many students confuse these three terms: speed, velocity and acceleration. Let us clear this step by step.
1. Speed
- Tells how fast something is moving
- Has only magnitude
- Does not include direction
Example:
“The car is moving at 40 km/h”
2. Velocity
Speed with direction
Has magnitude and direction
Example:
“The car is moving at 40 km/h towards the east”
3. Acceleration
- Change in velocity with time
- Can be due to a change in speed or direction
Comparison Table
| Quantity | Meaning | Direction Included? | Changes Cause Acceleration? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | How fast an object moves | No | No |
| Velocity | Speed with direction | Yes | Yes |
| Acceleration | Change in velocity | Yes | — |
Important Point for Students
- Change in speed → Acceleration
- Change in direction → Acceleration
- Change in both → Acceleration
So, acceleration depends on velocity, not just speed.
Positive, Negative, and Zero Acceleration

1. Positive Acceleration
When speed increases with time.
Example: A bike speeding up on an empty road.
2. Negative Acceleration (Deceleration)
When speed decreases with time.
Example: A car is slowing down near a signal.
3. Zero Acceleration
When velocity remains constant.
Example: A train moving at constant speed in a straight line.
Why Acceleration Is Important in Physics
Acceleration helps us understand:
- How vehicles start and stop
- How athletes improve performance
- How safety systems like airbags work
- How motion changes over time
Without acceleration, we cannot fully explain motion.
Why This Question Is Asked in Exams

Teachers ask acceleration questions because:
- It tests understanding of motion
- It connects speed and velocity
- It checks a real-life application
- It prepares students for higher physics concepts
Conceptual clarity matters more than formulas here.
Quick Summary for Students
- Acceleration means a change in velocity
- Velocity includes speed + direction
- Speed change or direction change causes acceleration
- Acceleration can be positive, negative, or zero
- Even constant speed can have acceleration
FAQs – Acceleration in Physics
1. What is acceleration in simple words?
Acceleration means how fast velocity changes with time.
2. Is acceleration only about increasing speed?
No. Decreasing speed and changing direction also cause acceleration.
3. Can an object have acceleration with constant speed?
Yes. If direction changes, acceleration exists.
4. What is negative acceleration?
Negative acceleration happens when speed decreases with time.
5. Why is acceleration important for students?
It helps understand motion, vehicles, sports, and exam concepts clearly.






