Recently updated on January 7th, 2026 at 07:48 am
Physics often sounds difficult, but some topics are actually very simple when explained properly.
Work, Energy and Power are such topics.
This article is written For Students of Class 8 and Class 9.
There is no heavy maths, no confusing formulas, and no exam fear.
By the end of this blog, you will clearly understand:
What work is
What energy is
What power is
How are they different
How are they used in daily life
Let’s start step by step.
What Is Work?
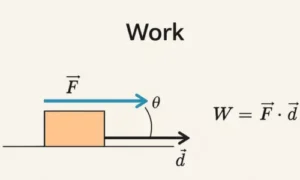
In physics, work is done only when a force causes movement.
Just applying force is not enough.
Movement must happen.
Simple Understanding
If you push a wall and it does not move, no work is done.
If you push a box and it moves, work is done.
Daily Life Examples
Lifting a school bag from the floor
Pulling a chair closer to you
Kicking a football and making it move
In all these cases:
A force is applied
The object moves
That is why work is done.
Important Point for Students
Holding a heavy bag without moving it feels tiring.
But in physics, no work is done because there is no movement.
This is where students usually get confused.
What Is Energy?

Energy is the ability to do work.
If you can do work, you have energy.
If you have no energy, you cannot do work.
Simple Way to Remember
No energy = no work
Energy is not something we see directly,
But we feel its effects everywhere.
Examples of Energy in Real Life
Food gives us energy to walk and run
A battery gives energy to a torch
Petrol gives energy to a bike
The Sun gives energy to Earth
Without energy, nothing can move or work.
Types of Energy (Class 8 Level)
You don’t need to memorise many types.
Just understand these common ones:
Muscular energy – energy from our body
Electrical energy – energy from electricity
Heat energy – energy due to heat
Light energy – energy from light
All these help in doing work.
What Is Power?

Power tells us how fast work is done.
It is not about how much work,
But how quickly the work is completed.
Simple Explanation
If two students lift the same bag:
One lifts it quickly
One lifts it slowly
Both do the same work.
But the student who lifts it faster has more power.
Easy Examples
A fast fan has more power than a slow fan
A bike that accelerates quickly has more power
A powerful mixer finishes work faster
Power is all about the speed of doing work, not strength.
Difference Between Work, Energy, and Power
Students often mix up these three terms.
Here is a simple way to separate them.
Work
Happens when force causes movement
Depends on movement
Example: pushing a moving cart
Energy
Ability to do work
Stored inside objects or living beings
Example: food, fuel, battery
Power
Speed of doing work
Depends on time
Example: fast machines have high power
One-Line Trick to Remember
Energy allows work
Work uses energy
Power shows how fast work happens
Real-Life Example Combining All Three
Imagine a student climbing stairs.
The student uses energy from food
The student does work by moving upward
If the student climbs fast, power is high
If the student climbs slowly, the power is low
Same stairs.
Same work.
Different power.
This example is very important for exams.
Common Mistakes Students Make

Let’s clear some common confusion.
Mistake 1: Thinking Effort Is Always Work
Feeling tired does not mean work is done in physics.
Movement is necessary.
Mistake 2: Mixing Energy and Power
Energy is not speed.
Power is speed.
A machine can have high energy but low power.
Mistake 3: Memorising Without Understanding
These topics are logic-based.
If you understand examples, formulas become easy later.
Why This Topic Is Important for Exams

Work, Energy, and Power:
Appear in Class 8 and 9 exams
Are asked in MCQs and short answers
Help in understanding higher physics later
Examiners mostly test:
Ensuring movement in work
Difference between energy and power
Daily-life examples
Understanding is more important than calculation here.
Quick Revision for Students

Work needs force + movement
Energy is the capacity to do work
Power is how fast work is done
If you remember this,
You can answer most questions correctly.
Questions and Answers
1. Is work done when you push a wall?
No. The wall does not move, so no work is done.
2. What gives us energy to do work?
Food gives energy to our bodies.
3. Can work be done without energy?
No. Energy is required to do work.
4. What does power tell us?
Power tells how fast work is done.
5. Who has more power: a fast or slow worker?
A fast worker has more power.