Have you ever wondered why a hot cup of tea cools after a while? Or, how does your refrigerator keep food cold? The solution is found in thermodynamics, a field of physics that describes how heat, energy, and work are related.
Thermodynamics may appear to be a complicated concept, but if you learn the fundamentals, it becomes fairly simple and exciting!
Also See: Electricity & Magnetism
What is Thermodynamics?
Thermodynamics is the study of how energy travels and takes different forms. It mostly deals with thermal energy (heat) and mechanical energy (work).
In simpler terms:
Thermodynamics is the science that explains how energy moves from one location to another and influences matter.
Real-World Examples of Thermodynamics
- When you boil water, heat energy converts liquid water to steam.
- When you drive a car, the fuel burns to provide energy that propels the vehicle.
- To keep food cold, heat is removed from the inside of the refrigerator.
Thermodynamics helps us understand all of these energy transformations!
The Four Laws of Thermodynamics (Made Simple)
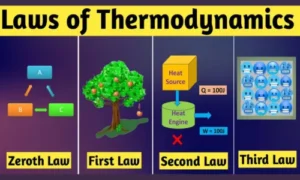
1. Zeroth Law – The Law of Thermal Equilibrium
- When two items are in thermal equilibrium with a third object, they are also in equilibrium with one another.
Simply put: if A = C in temperature, and B = C in temperature, then A = B.
Example: The temperature of a hot cup of tea and a thermometer gradually equalise.
2. First Law – Law of Energy Conservation
- Energy only changes forms; it cannot be created or destroyed.
The universe’s overall energy never changes.
Example: For instance, no energy is lost when wood burns; instead, chemical energy is converted into heat and light.
3. Second Law – Law of Entropy
- Heat naturally flows from hot to cold, and systems tend to grow more chaotic over time.
Ice melts in a warm environment, not the other way around.
For example, leaving a hot cup of coffee on the table causes it to cool down.
4. Third Law – Absolute Zero
- As the temperature approaches absolute zero (-273.15°C), particle movement comes to a near halt.
Complete stillness, with no residual heat energy.
Example: At absolute zero, atoms have the lowest conceivable energy.
Applications of Thermodynamics in Daily Life

- Air Conditioners – transfer heat out of rooms.
- Engines – convert fuel into motion.
- Power Plants – generate electricity using heat.
- Cooking – transfers heat to prepare food.
In physics, chemistry, engineering, and even biology, thermodynamics is essential!
Fun Facts:
1. The Earth’s primary source of thermodynamic energy is the Sun.
2. Your body turns food into energy in accordance with thermodynamic laws!
3. Thermodynamics is used by engineers to create motors, rockets, and even coffee makers!
Why Should Students Learn Thermodynamics?

Learning thermodynamics will assist you:
- Understand how machines and natural systems operate.
- Develop problem-solving and logical thinking skills.
- Prepare to work in science, engineering, and technology.
Conclusion
Thermodynamics explains how heat and energy circulate in everything, from your body to the stars. It is the science of comfort, mobility, and current technology. Once you understand its fundamental laws, you’ll notice thermodynamics everywhere in everyday life!






