Ever ponder why your favourite song may quickly improve your mood or why some songs evoke strong memories? The impact that music has on the human brain is significant. According to neuroscience, our love of music has its roots in the way our brains interpret sound, feelings, and memories.
How the Brain Processes Music
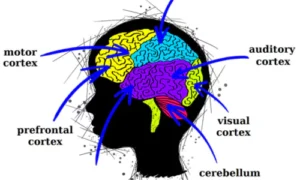
1. Auditory Cortex
- Located in the temporal lobe.
- Responsible for analysing pitch, rhythm, and melody.
2. Limbic System
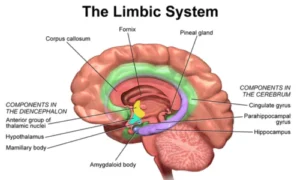
- Includes the amygdala and hippocampus.
- Connects music with emotions and memories, explaining why songs trigger feelings.
3. Motor Cortex
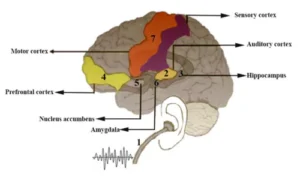
- Gets activated when you tap your foot or dance.
- Helps with rhythm and movement synchronisation.
4. Prefrontal Cortex
- Linked to decision-making and prediction.
- Engages when anticipating the next note or beat.
Why the Brain Loves Music
1. Dopamine Release
The reward system in the brain is triggered by music, which releases dopamine, the same “feel-good” neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and eating.
2. Emotional Regulation

Songs have the power to heal pain, soothe anxiety, and lower tension. Music therapy is a popular method for emotional recovery.
3. Memory Boost

Have you ever remembered lyrics from the past? This is because listening to music helps people with diseases like Alzheimer’s disease since it improves memory recall.
4. Social Connection

Traditional chants and contemporary concerts both use music to bring people together by stimulating brain regions associated with cooperation and camaraderie.
5. Cognitive Enhancement

Focus, inventiveness, and even language proficiency can all be enhanced by learning or listening to music.
Interesting Facts About Music and the Brain

- Babies may recognise musical patterns before they learn to speak.
- Musicians frequently have strong connections between their left and right hemispheres.
- Upbeat tunes can improve workout performance by stimulating motor neurons.
Conclusion
Our brain likes music because it activates numerous areas at once—sound, movement, memory, and emotion. Music is more than simply entertainment; it is an effective instrument for mental wellness, social bonding, and cognitive development. The neurobiology of sound demonstrates that music genuinely makes us human.
FAQs
1. Why does music make us feel emotional?
Because it activates the brain’s limbic system, which is tied to emotions.
2. Can music help improve memory?
Yes, music strengthens memory recall and is used in therapy for dementia patients.
3. Does playing an instrument change the brain?
Yes, it improves coordination, strengthens neural connections, and boosts creativity.
4. Why does music give us chills?
Chills occur when dopamine floods the reward system during emotionally powerful music.
5. Can music improve focus?
Yes, especially instrumental or classical music, which enhances concentration.






