Earthquakes are sudden shakings of the Earth’s surface caused by the movement of tectonic plates beneath it. They occur when stress in the Earth’s crust is released in the form of seismic waves.
An earthquake is a sudden and intense shaking of the Earth’s surface. It occurs when there is a sudden release of energy in the Earth’s crust, mainly caused by the movement of tectonic plates. This energy travels in the form of seismic waves, causing the ground to tremble. Depending on the magnitude of the earthquake, the shaking can be scarcely apparent or severe enough to inflict significant damage.
Why do earthquakes occur?

The movement of tectonic plates is the primary source of earthquakes. The Earth’s crust is made up of numerous massive chunks called plates, which move gently over its surface. When these plates meet, move past each other, or pull apart, the accumulated pressure is released as energy, causing an earthquake.
Other factors are:
1. Volcanic eruptions.
2. Landslides
3. Human activity, such as mining or major construction projects
Types of Earthquakes
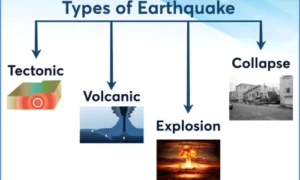
1. Tectonic Earthquakes – Caused by the movement of tectonic plates
2. Volcanic Earthquakes – Linked to volcanic activity
3. Collapse Earthquakes – Caused by cave-ins or underground mining
4. Explosion Earthquakes – Resulting from nuclear or chemical explosions
Measuring Earthquakes
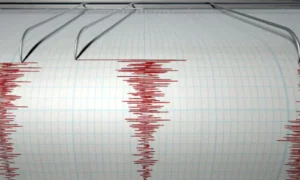
Earthquakes are measured using:
- Seismographs – instruments that detect ground motion
- Richter Scale – measures the magnitude (energy released)
- The Moment Magnitude Scale (Mw) is most accurate for large earthquakes
- Mercalli Intensity Scale – describes the observed damage
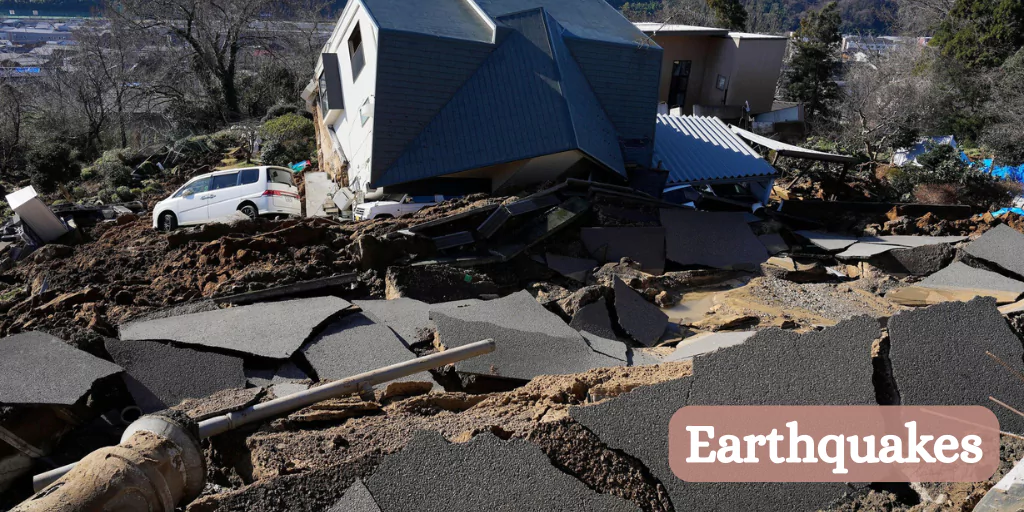
Effects of Earthquakes

- Ground shaking and cracking
- Building collapse
- Fires from broken gas lines
- Landslides and avalanches
- Tsunamis (if an earthquake occurs under the ocean)
- Loss of life and property
Earthquake Safety Tips

If You’re Indoors:
- Drop, cover, and hold on
- Stay away from windows and heavy furniture
- Don’t use elevators
If You’re Outdoors:
- Move to an open region free of buildings, trees, and electricity wires.
Before an Earthquake:
- Secure heavy items to the walls
- Keep an emergency kit ready
- Know evacuation routes
Commonly Asked Questions About Earthquakes
1. What is the main cause of earthquakes?
The most prevalent reason is the movement of tectonic plates across fault lines.
2. Can we predict earthquakes?
No, earthquakes cannot be predicted with exact timing and location, but scientists can identify areas with high risk.
3. What is the difference between magnitude and intensity?
- Magnitude: Measures the energy released
- Intensity: Measures the damage and human perception
4. Which country experiences the most earthquakes?
Japan, Indonesia, and Chile are among the most earthquake-prone countries.
Earthquake FAQ
Q1: What should I do immediately after an earthquake?
Make sure no one is hurt, stay off the phone unless required, and be ready for aftershocks.
Q2: Are aftershocks dangerous?
Yes. Aftershocks can cause further damage to weakened structures.
Q3: Why are some earthquakes more destructive than others?
Depth, location, population density, building quality, and local geology are all important considerations.
Q4: Can animals sense earthquakes?
Some animals seem to sense earthquakes seconds or minutes before they occur, but it’s not fully understood.
Q5: What is a fault line?
A fault line is a crack in the Earth’s crust where two tectonic plates meet.
Conclusion
Earthquakes are natural occurrences that can have terrible consequences. Understanding the causes, effects, and safety precautions is critical for risk reduction. While we can’t stop earthquakes, being prepared can save lives. Earthquakes are powerful natural disasters that can strike unexpectedly, causing significant devastation and loss. Understanding their causes, types, and effects, as well as how to be safe, can help considerably reduce the hazards. We cannot prevent earthquakes, but we can prepare, educate people, and create safer places. Awareness and preparedness are critical to surviving and mitigating the effects of these natural disasters.






tải 888slot app
August 6, 2025Thuật toán Random Number Generator (RNG) là trái tim công nghệ đảm bảo tính công bằng tại tải 888slot app . Đây không đơn thuần là một bộ sinh số ngẫu nhiên thông thường mà là hệ thống RNG tiên tiến được chứng nhận bởi iTech Labs – đơn vị kiểm định hàng đầu trong ngành. TONY12-12