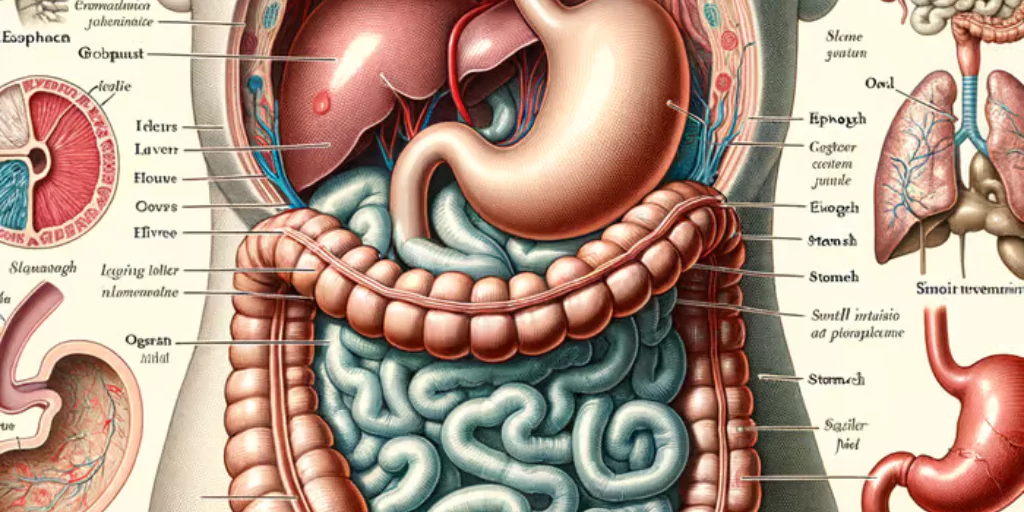
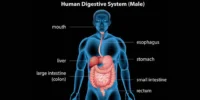
The human body uses a well-organised mechanism to digest meals and absorb nutrients. This system is referred to as the human alimentary system – the digestive tract, or the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. It is a continuous tube-like structure that extends from the mouth to the anus and is essential for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and removing waste.
Introduction to the Alimentary System
The alimentary canal is a muscular and hollow channel that measures around 30 feet in length. It consists of various specialised organs and glands that work together to digest food and extract energy. The voyage begins when food enters the mouth and concludes when undigested waste exits the body.
Major Parts of the Alimentary Canal
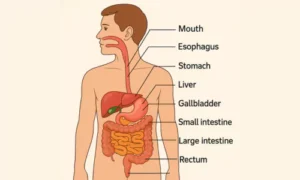
1. Mouth
Food intake begins here. Teeth break down food mechanically, while saliva begins chemical digestion.
2. Pharynx and Esophagus
These transport food from the mouth to the stomach using muscular contractions called peristalsis.
3. Stomach
A muscular organ that churns food and mixes it with digestive juices, including hydrochloric acid and enzymes.
4. Small Intestine
Divided into the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum are divided. It’s the main site of nutrient absorption.
5. Large Intestine (Colon)
Absorbs water and forms solid waste. Includes the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon.
6. Rectum and Anus
Stores and expels faecal matter through the process of defecation.
Accessory Organs That Support Digestion
- Salivary Glands: Produce saliva to moisten food and begin starch digestion.
- Liver: Produces bile to break down fats.
- Gallbladder: Stores bile and releases it into the small intestine.
- Pancreas: Secretes enzymes that further help in digesting carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Also see: Parts of the human digestive system
Main Functions of the Alimentary System
- Ingestion – Taking in food through the mouth.
- Digestion – Breaking down food into smaller molecules (mechanical and chemical).
- Absorption – Nutrients pass through the intestinal wall into the bloodstream.
- Assimilation – Cells use absorbed nutrients for energy and growth.
- Egestion – Removing undigested waste from the body.
Conclusion
The human alimentary system is essential for survival. It ensures that the food we eat is broken down into usable nutrients that fuel our daily activities and maintain body functions. Understanding this system helps us appreciate the complex and efficient way our body processes and utilises food.