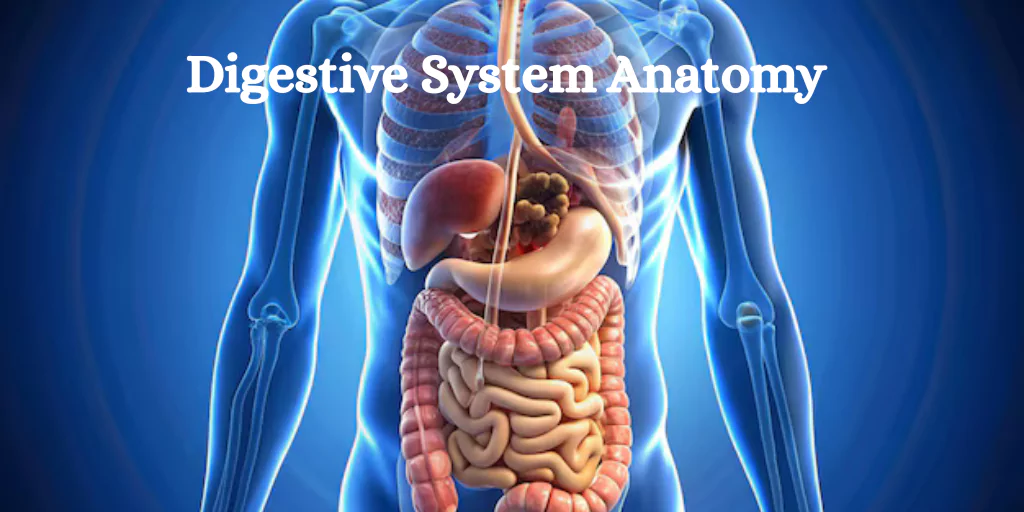
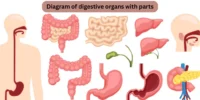
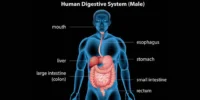
The digestive system is one of the most important systems in the human body. The body needs to convert the food we eat into nutrients that can be absorbed and used for energy, development, and repair. A digestive anatomy diagram illustrates all the major organs involved and their interactions, enabling a clearer understanding of this complex system.
What is anatomy?
Anatomy is the scientific study of the structure of living beings, specifically how their bodies are constructed and arranged.
In simpler terms:
Anatomy is the study of body parts and their location.
It informs you:
- What components comprise the body (such as bones, muscles, and organs)
- How are those parts connected or arranged?
- Their appearance and size.
What Is The Digestive Anatomy Diagram?
The digestive anatomy diagram is a labelled picture showing the structure and organisation of the digestive organs. It consists of the alimentary canal (also known as the gastrointestinal tract) and accessory organs that aid in the digestive process.
The figure often depicts the course that food takes from the mouth to the anus, emphasising how each organ contributes to digestion and nutrient absorption.
Main Parts Labelled in the Diagram
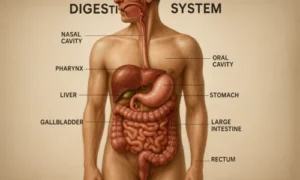
1. Mouth
- The entry point for food. Chewing and saliva begin the digestion process here.
2. Esophagus
- A muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach and pushes food down using a motion called peristalsis.
3. Stomach
- A sac-like organ that churns food with digestive juices, breaking it down into a semi-liquid form called chyme.
4. Small Intestine (Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum)
- Most digestion and nutrient absorption happen here. Digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver are added here.
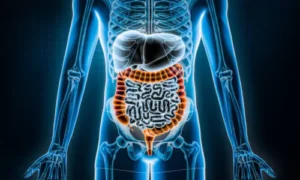
5. Large Intestine (Colon)Set featured image
- Absorbs water and minerals, forming solid waste (faeces).
6. Rectum and Anus
- The final section, where waste is stored and eventually eliminated from the body.
7. Liver
- Produces bile to help break down fats.
8. Gallbladder
- Stores and releases bile into the small intestine.
9. Pancreas
- Secretes digestive enzymes and regulates blood sugar by producing insulin.
Why the Diagram is Important
- Educational Tool: Helps students and medical professionals understand how digestion works.
- Health Awareness: Knowing where each organ is located helps people spot gastrointestinal problems.
- Visual Learning: Visual learning makes complex anatomy easier to understand by demonstrating the exact structure and flow
Conclusion
A digestive anatomy diagram is more than simply a graphic; it’s a guide to how your body processes food. By examining organs and their functioning, we acquire a greater knowledge of how our bodies fuel themselves. This diagram is a wonderful resource for students, teachers, and anybody interested in how digestion works.