Recently updated on November 7th, 2025 at 04:54 pm
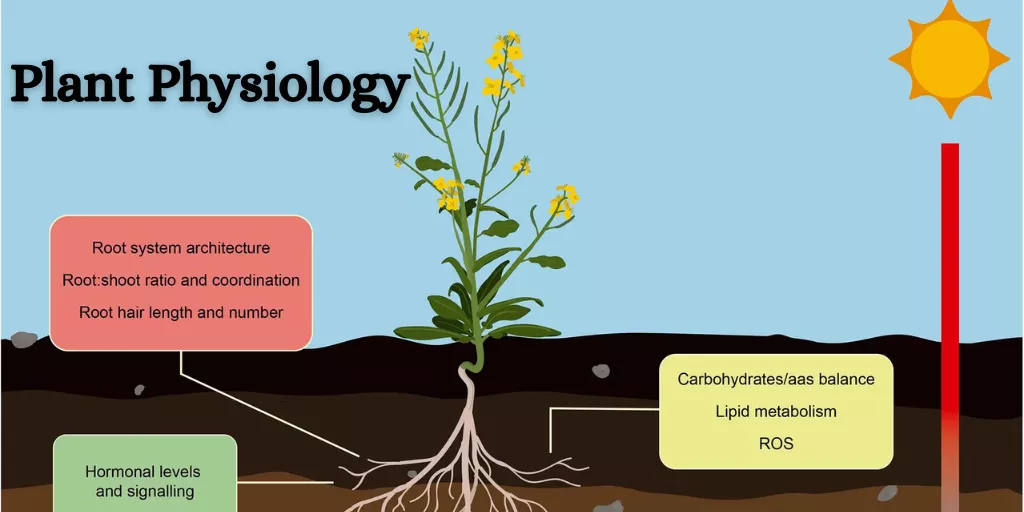
Plant physiology is a field of botany that examines plant functions and processes. It teaches us about how plants grow, develop, and respond to their surroundings. Plants, like humans and animals, have intricate mechanisms that help them survive, such as nutrient absorption, food production, and light response.
1. What is Plant Physiology?

Plant Physiology studies the biological processes that occur within plant cells and tissues. It focuses on understanding how plants carry out critical tasks like photosynthesis, respiration, water transport, and nutrient absorption.
Some of the main areas studied include:
- Photosynthesis
- Respiration
- Water and mineral nutrition
- Growth and development
- Plant hormones
- Environmental responses
2. Photosynthesis is the energy factory of plants
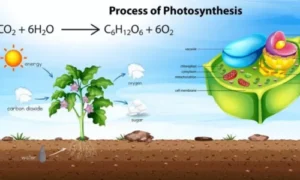
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants transform light into chemical energy. It primarily occurs in chloroplasts, where glucose and oxygen are produced from sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water.
Equation: 6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
This mechanism is the foundation of life on Earth since it supplies oxygen and nourishment to other living organisms.
3. Respiration: The Energy Release Process
Plants, like animals, can breathe. They use the glucose produced during photosynthesis to provide energy for growth and cellular activity.
Types of respiration:
- Aerobic respiration occurs in the presence of oxygen.
- Anaerobic respiration: Occurs without oxygen, mainly in root cells during waterlogging.
4. Water and Mineral Nutrition

Plants take water and minerals from the soil via their roots.
- Xylem transfers water and nutrients from roots to leaves.
- Phloem transports nourishment from leaves to other parts of the plant.
Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and magnesium are essential elements that contribute significantly to plant health and productivity.
5. Plant Growth and Development

Plant growth entails cell division, elongation, and differentiation. Internal and external factors that can influence growth include:
- Light
- Temperature
- Water availability
- Nutrients
Auxanometers are used to quantify growth at various phases, such as germination, blooming, and fruiting.
6. Function of Plant Hormones

Plant hormones (sometimes called phytohormones) are chemical messengers that regulate growth and development.
The main plant hormones include:
- Auxins promote cell elongation.
- Gibberellins promote stem development and seed germination.
- Cytokinins stimulate cell division.
- Abscisic acid: Controls stress and seed dormancy.
- Ethylene affects fruit ripening.
7. Environmental Responses in Plants

Plants respond to environmental cues such as light, gravity, touch, and water. These responses are called tropisms.
- Phototropism: A response to light.
- Gravitropism: A response to gravity.
- Thigmotropism: A touch response.
- Hydrotropism: A response to water.
These enable plants to adapt and thrive in changing circumstances.
8. The importance of studying plant physiology

Understanding plant physiology is critical in agriculture, forestry, and environmental conservation. It benefits scientists and farmers:
- Improve crop yields.
- Develop drought-resistant plants.
- Optimise fertiliser and water usage.
- Understand the impacts of climate change on plant health.
Conclusion
Plant Physiology highlights the interesting inner workings of plants, from how they produce food to how they interact with their surroundings. Studying these processes not only broadens our understanding of nature but also helps us develop a more sustainable future through better agricultural practices and environmental stewardship.